Crypto scams are any schemes that trick you into sending digital assets or approving wallet actions under false pretenses and they are hard to undo because most blockchain transactions are irreversible once confirmed.
This article is for everyday crypto users, from beginners to experienced holders, who want to recognize scams before funds leave their wallets. It focuses on the most common scam mechanics, red flags, and prevention steps you can use right now, not on recovering lost funds or covering every niche fraud variant.
Key Takeaways
- Losses are still accelerating: Recent FBI IC3 reporting puts crypto-related losses in the multi-billion-dollar range annually, driven primarily by investment fraud and social engineering, not technical hacks.
- Scams don’t look “technical”: Most succeed through pressure, impersonation, and fake authority, then lock losses in with irreversible on-chain actions.
- Red flags repeat: Urgent time pressure, crypto-only payment demands, off-domain links, remote-access requests, and unexpected wallet “approve” prompts account for the vast majority of cases.
- Irreversibility is the trap: Once a transaction or approval is confirmed, there is usually no undo button. Prevention beats recovery almost every time.
- The best single rule: Pause. Verify independently. Confirm on-chain. Scams collapse when you slow the timeline and check outside their links or instructions.
- If you only read one thing: Never share seed phrases. Never approve unknown contract permissions. Never install remote-access tools for “support.”
What Counts as a Crypto Scam (and Why Crypto Makes Them Hard to Undo)
Crypto scams mean any scheme where someone deceives you into sending digital assets or granting wallet permissions under pretenses, typically by exploiting trust, urgency, or technical confusion. Once you confirm a transaction on most public blockchains, there is no built‑in “undo,” which is why prevention matters more than recovery.
Why crypto is so attractive to scammers:
- Irreversible transfers: Most blockchain transactions are final once confirmed, so victims cannot simply call a bank to reverse a fraudulent crypto payment.
- Pseudonymity: Wallets are visible on‑chain, but they are not directly tied to real‑world identities, which lets criminals move funds without immediately exposing who they are.
- Speed and cross‑border reach: Crypto moves value across borders in minutes, so scammers can receive funds and push them through mixers, bridges, and offshore platforms before law enforcement can react.
- Scalable infrastructure: Fraud groups reuse phishing kits, fake platforms, AI‑generated personas, and scripted chats to target thousands of victims in parallel.
In practice, most crypto scams are a mix of psychology, distribution, and a technical trap: a human story that builds trust or fear, a channel that reaches you at scale (DMs, apps, ads), and a final step where you click a link, scan a QR code, or sign a transaction that hands over control of your money.
The Red Flags Checklist (Save This)
 All Crypto Scams Exhibit Certain Red Flags
All Crypto Scams Exhibit Certain Red FlagsCopy this list to your phone notes or pin it because scammers bank on you acting fast without checking these signals first. Spot any two or more? Walk away and verify independently. These cover 95% of crypto attacks reported to the FTC and IC3.
Universal red flags (works for nearly every scam)
Certain signals are like guaranteed returns, and time pressure is often spotted in all kinds of scams within the Web3 industry.
- Urgency or time pressure: "Act now or lose access," "last spot," or countdown timers to rush you.
- "Guaranteed returns": Promises of fixed high yields like "20% weekly" with zero downside talk.
- Move to Telegram/WhatsApp: Quick shift from main platform to private, encrypted chat.
- Pay in crypto only: Insistence on specific coins or wallet addresses, no fiat options.
- Remote access requests: AnyDesk, TeamViewer, or "screen share to fix" your issue.
- Off-domain URLs/misspellings: binanace.com, meta-mask.io, or QR codes to unknowns.
- "You must approve" prompts: Unexpected wallet signatures to "unlock," "verify," or "claim."
- Refusal to verify: Dodges video calls, ID checks, or official contact confirmation.
The “Stop. Verify. Confirm.” 60-second routine
Even if you think it is legit, always keep a record of the documents, terms, and interactions for your own safety. Remember, extra due diligence costs you nothing.
- Stop and screenshot everything: Hit pause. Capture screen, URL bar, chat, everything to confirm or document.
- Verify identity and domain independently: Type the official site from memory/bookmarks. Never use their links.
- Confirm on-chain actions before signing: Paste the address into the explorer. Check history, simulate tx, read permissions plain-text.
Common Crypto Scams in 2026
 A Look At Some Of The Most Common Crypto Scams
A Look At Some Of The Most Common Crypto ScamsThe way crypto users are scammed has changed with the industry itself but patterns stick to proven tactics: Fake urgency, trust abuse, and technical tricks that lock in losses fast.
In 2026, you can expect more AI deepfakes, cloned apps, and cross-chain traps, but the core defenses — pause, verify, check on-chain — still block most attacks. This section breaks down the top threats with exact steps for each.
Phishing and “Quishing” (QR code phishing)
What it is: Attackers send emails, DMs, or posts with fake login pages, wallet connect screens, or QR codes that drain your accounts when scanned or clicked.
How it works:
- Spoofed emails mimic exchanges or wallets with "urgent security alerts."
- QR codes in ads or messages link to phishing sites when scanned.
- Fake "Connect Wallet" popups appear on cloned DApps or NFT mint pages.
- Clipboard malware swaps your paste address mid-transaction.
- Multi-stage: First steal login, then push for 2FA reset or seed phrase.
Red flags:
- Unsolicited emails/DMs with links or QR codes about account issues.
- Domain mismatches like "binanace.com" or "0x00... QR scam."
- Wallet connect requests from unknown sites or apps.
- Pressure to "scan now to claim" or "verify before lockout."
- Browser warnings or certificate errors on the site.
- Requests for the seed phrase after "login."
How to avoid:
- Bookmark official sites; never click links in messages.
- Use a hardware wallet QR scanner confirmation.
- Enable browser extensions like wallet guards.
- Verify URLs character-by-character before connecting.
- Test small dummy transactions first.
If it happened:
- Change all passwords and enable 2FA immediately.
- Revoke all wallet sessions and approvals.
- Scan the device for malware.
- Report tx hash to the exchange and IC3.
- Monitor credit and move funds to a new wallet.
Wallet-Approval Drainers (Permit/Approve scams, SetApprovalForAll)
What it is: Malicious DApps or NFTs trick you into signing approvals that let attackers drain your entire wallet over time.
How it works:
- "Free mint" or "claim" sites request unlimited token spend approval.
- ERC-20 Permit signatures grant spend allowance without gas.
- NFT scams use SetApprovalForAll for operator access.
- Drain occurs later via automated scripts that trigger your approvals.
- Cross-chain bridges with hidden drain functions.
Red flags:
- Any "approve" for unlimited amounts on unknown contracts.
- Mint/claim sites with no clear team or audit.
- "Connect to continue" on random links.
- Permissions for tokens you don't own.
- High gas for simple actions.
How to avoid:
- Check every signature in a readable format (use simulators).
- Revoke approvals weekly via tools like Revoke.cash.
- Set low allowances, never unlimited.
- Avoid free mints from Twitter ads.
- Use multisig or watch-only wallets for DeFi.
If it happened:
- Revoke all approvals immediately.
- Transfer remaining funds to a fresh wallet.
- Check on-chain for drainer contracts.
- Report to wallet provider.
- Freeze exchange accounts linked.
See our top picks for the most secure crypto wallets for better protection.
SIM Swapping (Phone-number takeovers)
What it is: Criminals social-engineer your mobile carrier to port your number to their SIM, stealing 2FA logins.
How it works:
- Attacker bribes an insider or guesses security questions.
- Port your number silently during off-hours.
- Intercept SMS 2FA for exchanges and banks.
- Reset passwords and drain linked accounts.
- Often pairs with phishing for full access.
Red flags:
- Sudden loss of phone service without warning.
- Unexpected 2FA prompts or login alerts.
- Carrier texts about "account updates."
- Friends report odd messages from your number.
How to avoid:
- Set carrier PIN or port-out freeze.
- Use authenticator apps, not SMS.
- Hardware keys (YubiKey) were supported.
- List only 1-2 recovery emails/phones.
- Monitor the carrier account weekly.
If it happened:
- Contact the carrier immediately to reverse port.
- Change all 2FA to app-based.
- Secure email first (often SIM target).
- Report to IC3 and exchanges.
- Get a new number if possible.
Pig-Butchering (Romance + Investment hybrid)
What it is: Long-term grooming via dating apps or social media leads to fake investment platforms that drain savings.
How it works:
- A fake profile builds a relationship over weeks.
- Introduces "trading mentor" or signals group.
- Directs to a fake app showing fake profits.
- Escalates to larger deposits.
- "Tax" or "license" fee to withdraw, then vanish.
Red flags:
- New online contact pushes crypto investing fast.
- Fake platform only accepts deposits, shows gains.
- VIP groups on Telegram with signals.
- Withdrawal blocks need more funds.
- Reluctance to meet in person.
How to avoid:
- Never invest via social contacts.
- Test withdrawals early on any platform.
- Stick to the top exchanges only.
- Reverse-image search profile pics.
- Share suspicious apps with scam trackers.
If it happened:
- Stop all contact and block.
- Document chats and tx for reports.
- Report to FTC/IC3 immediately.
- Secure all accounts.
- Seek counseling for the emotional side.
Celebrity/Deepfake Promotions and Fake Giveaways
What it is: Cloned accounts or AI videos of influencers promise "send 1 ETH, get 2 back."
How it works:
- Deepfake livestreams on YouTube/Twitch.
- Impersonator Twitter with checkmark.
- "Double your money" via wallet send.
- Fake airdrops needing seed or approval.
- Coordinated shill armies.
Red flags:
- Celeb account DMing you personally.
- "Send to this address to verify."
- Livestream with donation QR/wallet.
- No official announcement page.
- Too good returns in comments.
How to avoid:
- Verify via official channels only.
- Never send to "double back."
- Check the account creation date.
- Use on-platform verification badges.
- Report impersonators immediately.
If it happened:
- Do not send more.
- Report tx and account.
- Warn your network.
- Change exposed wallets.
Fake Support and Remote-Access “Help”
What it is: Popups or calls claim your account is hacked, leading to a remote tool install or seed share.
How it works:
- Fake error screen with support number.
- "Technician" requests AnyDesk/TeamViewer.
- Steals seed, screenshots, or keystrokes.
- Drains while you watch.
- Often, after phishing login.
Red flags:
- Unsolicited support calls or pop-ups.
- "Share screen to fix."
- Seed phrase requests.
- Urgency about frozen funds.
- Bad accents or scripts.
How to avoid:
- Official support via app only.
- Never share remote access.
- Close the browser, restart the device.
- Use incognito for checks.
- Hardware wallet for storage.
If it happened:
- Disconnect the internet.
- Change all credentials.
- Run a full malware scan.
- Report to real support.
- Fresh OS install if needed.
Fake Exchanges, Fake Apps, and Lookalike Websites
What it is: Clones of Binance/Kraken with the same logos, pushing "tax" fees on fake withdrawals.
How it works:
- An ad or QR leads to a fake site.
- Fake login steals creds.
- App store malware versions.
- "Withdrawal fee" loops.
- Support bots collect more data.
Red flags:
- Unknown app urging download.
- Withdrawal needs a "license."
- No 2FA options.
- Odd URL or app permissions.
- Poor grammar in support.
How to avoid:
- Download from official stores only.
- Test a small withdrawal first.
- Check app signatures.
- Use official links always.
- Reputation search before deposit.
If it happened:
- Change creds on real accounts.
- Report a fake domain.
- Scan all devices.
- Monitor bank links.
Check out the most scam-immune crypto platform based on our research.
Malware and Copy-Paste Clipboard Hijackers
What it is: Software swaps your copied wallet address with the attacker's mid-send.
How it works:
- Malicious extension or email attachment.
- Monitors the clipboard for addresses.
- Replaces with a similar-looking one.
- Executes on paste-confirm.
- Often bundles with fake apps.
Red flags:
- Device slowdowns or popups.
- Address changes on second look.
- Unknown extensions.
- High CPU usage from the browser.
How to avoid:
- Verify address first/last chars twice.
- Use the address book whitelists.
- Antivirus plus extension audit.
- No pirated software.
- Hardware paste confirmation.
If it happened:
- Wipe and reinstall the OS.
- Change all wallets.
- Scan external drives.
- Report malware sample.
Rug Pulls and Exit Scams (Token and DeFi)
What it is: Devs launch a token/pool, hype it, then drain liquidity or dump supply.
How it works:
- Anonymous launches with fake audits.
- Liquidity pull via unlocked pools.
- Admin mints extra tokens.
- Bridge to drain TVL.
- Docs vanish post-rug.
Red flags:
- Anonymous team, no lockups.
- Weird tokenomics (high dev share).
- Unlocked LP on DEX tools.
- Fake TVL via flashloans.
- Hype without utility.
How to avoid:
- Check LP locks on Rugcheck.
- Verify team doxx/Audits.
- Small position only.
- Track supply on the explorer.
- Exit on first profit take.
If it happened:
- Sell any remainder fast.
- Report to DEX and trackers.
- Tax loss harvest.
- Learn tokenomics next time.
Pump-and-Dump Groups (Coordinated hype)
What it is: Telegram groups signal buys on low-liquidity tokens and dump on retail entry.
How it works:
- Paid shills tweet/pump.
- Volume spikes, price 10x.
- Insiders exit at the top.
- Token crashes 90%.
- Repeats on new coins.
Red flags:
- Sudden Telegram invites.
- "Buy now" with no research.
- Illiquid pairs spiking.
- Dev sells during the pump.
- Exit liq warning.
How to avoid:
- Ignore signal groups.
- DYOR token first.
- Avoid low-volume pumps.
- Set tight stops.
- Stick to blue chips.
If it happened:
- Hold or tax loss.
- Blacklist the group.
- Report to exchange.
Ponzi vs Pyramid vs “HYIP” (Clarify the difference)
What it is: Ponzi pays early investors with new money; pyramid requires recruitment; HYIP ("high yield investment") mixes both with fake returns.
How it works:
- Ponzi: "Platform" shows gains from new deposits.
- Pyramid: Earn by signing up friends.
- HYIP: Daily "interest" until collapse.
Red flags:
- Returns from "new members."
- No clear product.
- Unsustainable yields.
- Recruitment focus.
How to avoid:
- Math check: 2% daily compounds to 1375% yearly—impossible.
- Demand proof of reserves.
- Test a small withdrawal.
If it happened:
- Withdraw early if possible.
- Report to SEC/CFTC.
Cryptojacking (Silent mining on your device)
What it is: Malware mines coins using your CPU/GPU without consent.
How it works:
- Drive-by script on sites.
- Fake extension.
- Runs in the background.
- Spikes' power bill.
Red flags:
- CPU at 100%, overheating.
- Fan noise constant.
- The battery drains fast.
- Unknown processes.
How to avoid:
- Adblock Plus NoScript.
- Update OS/browser.
- Task manager checks.
- VPN for public WiFi.
If it happened:
- Kill processes.
- Full scan.
- Change passwords.
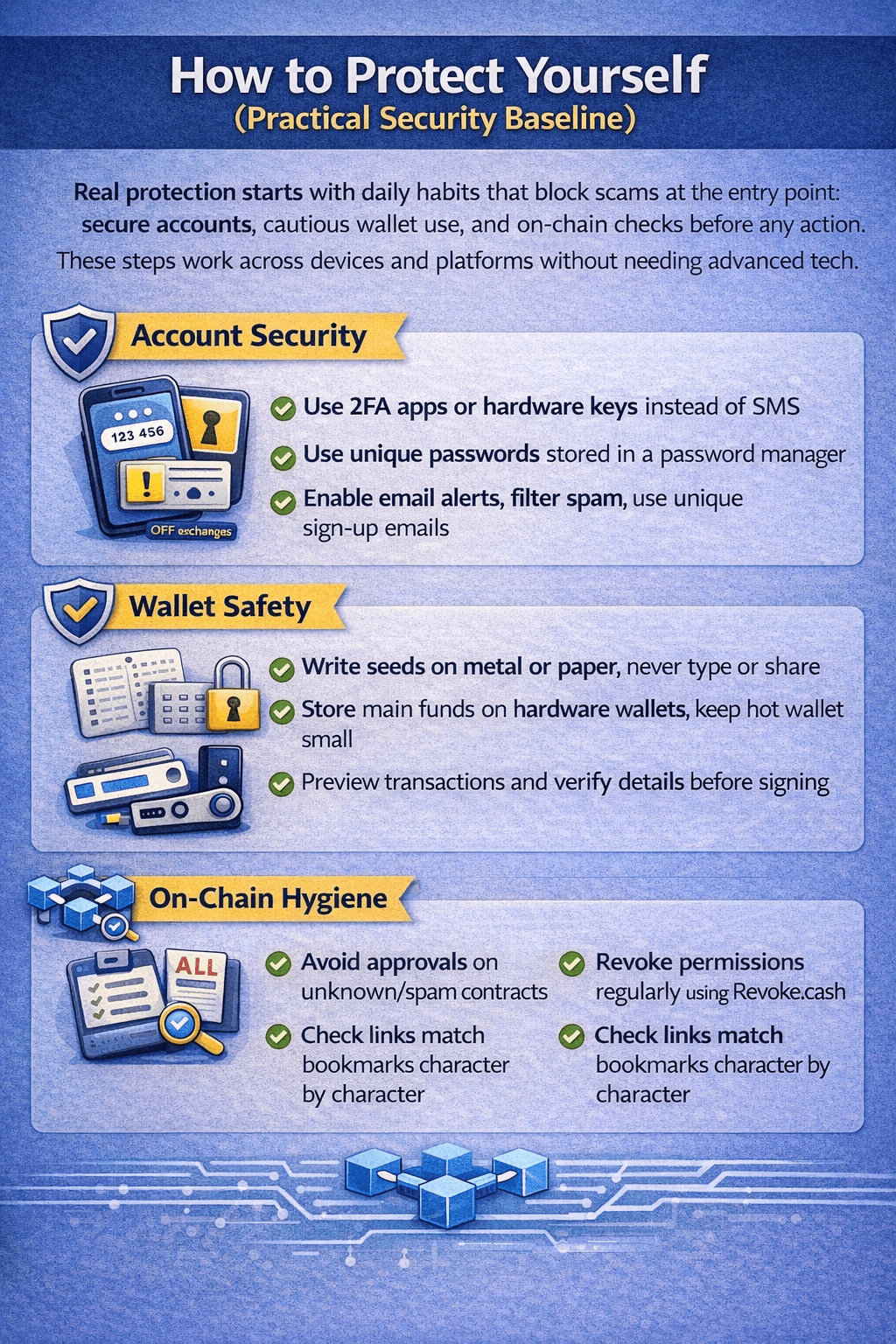
How to Protect Yourself
Real protection starts with daily habits that block scams at the entry point: secure accounts, cautious wallet use, and on-chain checks before any action. These steps work across devices and platforms without needing advanced tech.
 Avoid Any Links or Attachments from Suspicious Emails, Text Messages or Social Media
Avoid Any Links or Attachments from Suspicious Emails, Text Messages or Social MediaAccount security (exchange and email)
Exchanges and email act as the front door to all crypto holdings, so lock them down first.
- Use phishing-resistant 2FA like authenticator apps or hardware keys instead of SMS where exchanges support it.
- Store unique, long passwords in a manager like 1Password or Bitwarden and never reuse across sites.
- Treat email as your master key: enable login alerts, filter spam, and use alias emails for crypto signups since inbox compromise often leads to account takeovers.
Wallet safety (self-custody)
Self-custody gives control but demands discipline, focus on seed handling and storage separation to avoid total loss.
- Write seed phrases on metal or paper, store them in multiple secure locations, and never type them digitally or share them with anyone.
- Move holdings off exchanges to hardware wallets for amounts you cannot afford to lose; keep hot wallets small for daily use.
- Preview transactions in plain text and simulate them when possible to see exact transfers before signing.
On-chain hygiene (permissions, links, and signing)
On-chain actions lock in forever, so build habits that catch traps before you click send.
- Skip approvals on unknown contracts; Set temporary low limits if needed.
- Check and revoke old permissions monthly using sites like Revoke.cash or Etherscan.
- Take 30 seconds to confirm links match bookmarks and signatures show clear actions, no blind signing under pressure.
If You Were Scammed (Do This in Order)
Speed matters most after a scam. Follow these steps in sequence to cap damage, gather proof, and start recovery where possible. On-chain losses rarely reverse fully, but quick action can freeze exchange-held funds, block follow-on attacks, or support investigations. One must skip the emotions at first and treat it like containing a fire.
 If Scammed, Act Fast, Stop Payments & Gather Evidence
If Scammed, Act Fast, Stop Payments & Gather EvidenceContain the damage (first 30 minutes)
Act inside the first window when holds or revokes still work, and always prioritize stopping the bleed over anything else.
- Halt all transfers and disconnect wallets from dApps, sites, or browsers right away.
- Log out of every account and revoke active sessions on exchanges and wallets.
- Revoke all token approvals using block explorers or Revoke.cash to stop delayed drains.
- Reset passwords and 2FA on email/exchanges—start with email since it unlocks everything else.
- Move any remaining funds to a new, clean wallet if a device compromise seems likely.
Document everything (what to collect)
Proof builds your case. So collect chain-of-events data systematically for reports and any recovery shot.
- Pull transaction hashes, addresses, amounts, networks, and timestamps directly from explorers like Etherscan or Solscan.
- Screenshot chats, emails, sites, QR codes, and popups—capture full screen with URLs, dates, and context visible.
- Note all domains, social handles, phone numbers, wallet addresses, and exact instructions they gave you.
- Export chat logs if on Telegram/Discord and save payment proofs or fake platform screenshots.
Report it (where to report)
Reports feed databases that track scammers, file everywhere relevant to maximize pattern matches and freezes.
- FBI IC3 at ic3.gov: File investment fraud details with full tx proofs—they track crypto patterns.
- FTC ReportFraud at ReportFraud.ftc.gov: Report consumer scams like fake support or apps.
- CFTC resources at cftc.gov: Submit trading platform or "investment" complaints.
- SEC tips at sec.gov/tcr: Use for securities-related fraud like fake tokens or HYIPs.
- DFPI Scam Tracker at dfpi.ca.gov: Match your case to known patterns and add it publicly.
Notify your specific exchange or wallet provider immediately per FTC guidance—they may freeze outflows.
Reality check on recovery (set expectations)
Temper hopes with facts, so understand windows and traps to avoid round two losses.
- Recovery works best if funds sit on a compliant exchange, central bank wires reverse (under 24h), or law enforcement freezes mixers quickly.
- Most pure on-chain transfers stay gone forever due to blockchain design.
- Beware "recovery services" cold-calling you—they charge upfront fees and steal more in 90% of cases; stick to official reports only.
Recent Case Studies (2024–2025)
Real cases from DFPI trackers, IC3 reports, and blockchain forensics show how scams hit even careful users; each one boils down to skipping one routine check. These 2024-2025 examples focus on fresh patterns like AI clones and app fakes; study the miss and fix it today.
 A Look At Some Of The Top Scams of 2024-2025
A Look At Some Of The Top Scams of 2024-2025 “Confidence scam” networks got big enough for record seizures (2024)
A major U.S. investigation led to what the DOJ described as the largest-ever seizure tied to crypto confidence scams, with stablecoins used to move and park victim funds. The same reporting cycle shows crypto investment fraud remains a top driver of losses.
What the victim missed
- “Relationship first, money second” is a scam pattern, not a love story
- They trusted screenshots and dashboards instead of verifiable withdrawals
- They paid extra “fees” to unlock withdrawals (classic stall tactic)
How do you avoid it
- Treat any “mentor” who routes you to a platform as a threat
- Run a withdrawal test early, then again after profits appear
- If withdrawal requires a “tax/license/security fee”, stop
WhatsApp “signals group” → fake trading site → “pay 30% tax to withdraw” (DFPI, 2024–2025 pattern)
A California complaint describes the now-common flow: WhatsApp group + trading signals + fake platform + sudden tax demand before withdrawal. This is pig-butchering with a group-chat skin.
What the victim missed
- “Signals groups” are distribution, not credibility
- The “tax” was a lever to extract one last payment
- The platform had no real regulatory footprint or reputation trail
How do you avoid it
- No trading via WhatsApp/Telegram groups, full stop
- Verify the platform independently (entity, history, reviews, domain age)
- Any “tax to withdraw” = treat funds as already gone, shift to reporting
Lookalike exchange UI + stolen branding to look legit (DFPI “VOEX” example)
One DFPI complaint shows a fake platform mimicking a real trading interface while stealing a legitimate company’s logo to borrow trust quickly.
What the victim missed
- A slick UI is cheap; verification is the hard part
- Brand assets can be stolen in minutes
- “Looks like Binance/Kraken” is meaningless without domain and entity checks
How do you avoid it
- Only use exchanges from official app-store publisher pages and official domains
- Check the domain character-by-character, then confirm via official social/site links
- Do a small deposit + small withdrawal before anything else
Deepfake livestream “giveaway” raised real money in hours (2024)
Researchers tracked a YouTube deepfake livestream scam that pulled in tens of thousands via the oldest trick in crypto: “send X, receive 2X.” Deepfakes made the hook look more convincing, not more real.
What the victim missed
- Livestream authority is a fake authority
- QR codes + urgency are designed to bypass thinking
- Real brands don’t run “double your crypto” events
How do you avoid it
- Never send funds to “verify” or “activate” a giveaway
- Confirm via an official announcement page (not a reposted clip)
- Treat livestream QR codes as hostile by default
Bitcoin ATM fraud exploded (2024–2025), powered by impersonation scripts
FTC data shows Bitcoin ATM scams ramped hard, with high median losses reported in early 2024. FBI-linked reporting shows the trend stayed brutal through 2025, largely driven by government/bank/tech-support impersonation that pushes victims to “protect funds” by feeding cash into an ATM.
What the victim missed
- “Move your money now” is the scam, not the solution
- Paying through a Bitcoin ATM is designed to be irreversible
- Impersonation works because victims don’t verify through official channels
How do you avoid it
- If someone tells you to use a Bitcoin ATM, hang up
- Call the institution back using the number on the back of your card
- Tell older family members: “No legit agency takes payment via crypto ATM.”
Conclusion
Crypto scams keep changing their costumes, but the mechanics stay familiar. Pressure, trust, and a final irreversible click still do most of the damage. The scale of losses makes that clear, yet the defenses are boringly effective when used consistently. Slowing down, verifying domains and identities yourself, and reading exactly what you are signing breaks the scammer’s timing advantage. Most attacks fail when you refuse to be rushed and insist on understanding the action in plain terms before approving it.
The point of this guide is not to turn you paranoid, but predictable in the right way. Build habits that assume any link, prompt, or “support” request could be hostile until proven otherwise. Accept that recovery is rare and prevention is where nearly all money is saved. If you internalize just a few rules and apply them every time, you reduce your risk dramatically. What follows is a glossary you can use as a fast reference when something feels off and you need clarity before acting.
Scam Glossary (Fast Definitions)
Quick reference for crypto scam terms, bookmark for when ads, DMs, or sites trigger doubt. Each definition includes the core mechanic and one dead giveaway sign to spot it fast.
- Pig-butchering: Long grooming via dating apps or social media builds fake trust, leads to a phony trading platform showing gains, ends with blocked withdrawals and ghosting. Spot it: New contact pushes "investment tips" within days.
- SIM swap: Attacker bribes or tricks your carrier to transfer your phone number to their SIM, hijacking SMS 2FA codes for account takeovers. Spot it: Sudden service loss or weird carrier texts.
- Wallet drainer/approval phishing: A Malicious dApp or NFT site gets you to sign "approve" permissions that let attackers spend your tokens later. Spot it: Unlimited spend requests on random contracts.
- Rug pull: Token devs hype a launch, attract buyers, then drain the liquidity pool or dump the premined supply, crashing the price to zero. Spot it: Unlocked LP or anonymous team with high dev allocation.
- Honeypot token: Scam coin lets anyone buy but blocks sales through coded traps like high taxes or blacklists. Spot it: Price pumps, but your sell tx fails with odd errors.
- Recovery scam: Follow-up fraud where "experts" contact victims promising to trace stolen funds—for hefty upfront fees that vanish too. Spot it: Unsolicited offers to "recover" after a loss.
- Cryptojacking: Hidden malware or site scripts mine coins using your CPU/GPU power without consent, spiking your electric bill. Spot it: Constant 100% CPU or mystery browser tabs.





