Aave Review: Decentralised Lending Platform
With the state of the world economy, many people are considering decentralized Finance (DeFi) as an alternative to traditional Finance. Indeed, DeFi has been a scorching hot topic in crypto for a while, and it's gradually gaining more adoption from individuals and institutions. Cryptocurrency lending protocols such as Compound, MakerDAO, Euler, and Aave have been the main attractions to this financial spectacle with good reason.
We first wrote about the Aave project in 2019, when it was known as ETHlend, and the native token was LEND. The project has evolved over the years, with a rebranding of its native LEND token to the AAVE token. As you will see in this Aave review, Aave is not "just another cryptocurrency lending platform" but is one of the pioneers in DeFi.
"Your assets, secured: Audited by the world's leading security firms, security of the Aave Protocol is the highest priority." Source: Aave
What is Aave?
Aave (pronounced "ah-veh") is an open-source liquidity protocol, a decentralized cryptocurrency lending platform. It was the first DeFi lending protocol when it launched its first mainnet as ETHlend in 2017 (before DeFi became a "thing").
Initially, Aave was designed to work on Ethereum with ERC20 tokens and has expanded its scope since then to include many chains in the EVM ecosystem.
Aave means "ghost" in Finnish. Hence, cartoon-like ghosts appear on the Aave website. Stani Kulechov founded the original company in 2017 and quickly became passionate about working with leading developers from other projects within the DeFi space.

Kulechov is hyper-focused on ensuring the platform is attractive to institutional and retail investors, inside and outside the cryptocurrency industry.
To briefly recap, ETHlend was a peer-to-peer marketplace where borrowers and lenders could negotiate terms without a third party thanks to smart contracts. The platform was moderately successful, but the Aave team decided they could improve the platform and were “ready to be serious players” in the DeFi space.
This decision led to the launch of the Aave mainnet in January 2020, introducing a completely new protocol and a few novel features that changed DeFi forever.
In March 2022, with the launch of V3, Aave introduced a feature called "Portal," enabling Aave to work smoothly across several blockchains. So, if you're using AAVE, you can join in lending and borrowing on other chains, such as Avalanche.
In January 2023, the Aave governance members gave unanimous approval for the deployment of the V3 iteration of the protocol on the Ethereum network. The V3 release introduces fresh technical capabilities and advantages, encompassing enhanced capital efficiency, expanded collateral choices, and refined gas optimization enhancements.
2023 was a busy year for Aave, after the deployment of V3 to Ethereum, they also announced the activation of GHO stablecoin in July and released a new governance model for the decentralized social media platform Lens Protocol later in the year.
How Does Aave Work?
Aave operates as a decentralized financial system. It allows individuals to lend and borrow digital money and valuable items without a central authority. Lenders make extra money, while borrowers pay a small additional amount when they borrow.
Traditionally, when you needed a loan, you'd head to a bank or a financial institution. The bank will assess your creditworthiness based on your financial status and credit history to decide if your financial status is safe enough for a loan. Then, you would need to provide something valuable as security (like your car's title for a car loan), and in return, the bank would lend you the money. Each month, you'd pay back the money you borrowed along with interest.
In DeFi (Decentralized Finance), the lending process differs because no bank is involved, and your identity is pseudonymous. Brick-and-mortar and people-powered banks are replaced with smart contracts. Smart contracts may sound complicated, but they are just computer code that instructs Ethereum what operations to perform. Coin Bureau has an excellent breakdown of smart contracts on its website.
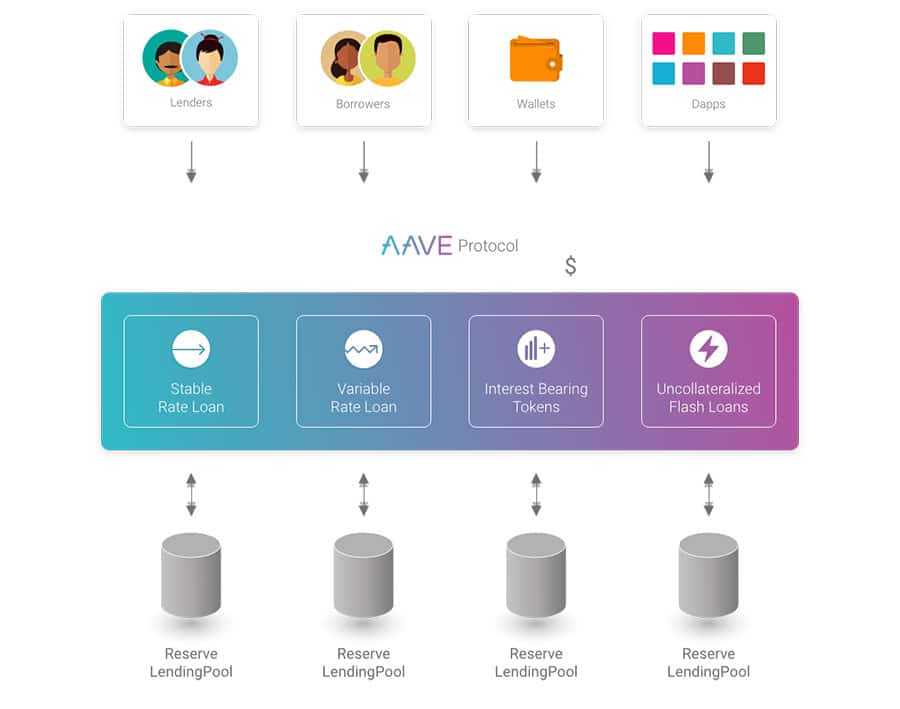
DeFi focuses on eliminating intermediaries regarding things like trading assets, making agreements for future trades, and even saving money.
In ETHLend, users borrow cryptocurrency from real people instead of going cap in hand to the big financial institutions. Aave replaces people with a pool-based strategy. Lenders with spare digital assets deposit them to a pool, which is an Aave smart contract that aggregates all the deposits for different assets from the lenders. Anyone can borrow the funds from the pool after pledging sufficient collateral.
Remember that all value exchange occurs in digital assets, and no fiat currencies are involved. The pool smart contract charges interest to borrowers and pays it to lenders. If you think about it, Aave pools funds and distributes them to lenders just like banks, but there are key infrastructural nuances here that I have summarized in the following table:
| Feature | Aave | Traditional Banks |
|---|---|---|
| Collateralization | Loans are over-collateralized, requiring borrowers to lock up assets worth more than the loan. | Loans can be under-collateralized or unsecured, based on the borrower's creditworthiness. |
| Interest Rates | Interest rates are algorithmically determined based on supply and demand of the assets within the pools. | Interest rates are set by the bank and influenced by central bank rates, market conditions, and the borrower's credit score. |
| Asset Accessibility | Provides access to a wide range of cryptocurrencies for lending and borrowing. | Primarily deals with fiat currencies and traditional asset classes. |
| Speed of Transactions | Transactions can occur almost instantly, depending on the blockchain's speed and congestion. | Loan approval and disbursement processes can take days to weeks. |
| User Anonymity | Allows for pseudonymous transactions without the need for a traditional credit check. | Requires personal identification and credit checks for loan approval. |
| Global Accessibility | Available globally to anyone with an internet connection and compatible wallet. | Access can be limited by geography, regulatory restrictions, and the need for a bank account. |
| Governance | Decentralized governance where token holders can vote on changes to the protocol. | Centralized decision-making through the bank's management and regulatory bodies. |
| Risk Management | Users are responsible for managing their own risk, especially concerning collateral liquidation. | Banks have dedicated teams for risk assessment and management, and offer various insurance products. |
Pseudonymity is a critical challenge for decentralized lending protocols. If Aave knows nothing about the borrower's identity, how can it safely lend money out? Like other lending protocols within the space, Aave offers overcollateralized loans, meaning that a user must lock a larger amount of collateral (in USD) than the loan. This amount depends on the asset and ranges from 50-75%.
For example, suppose you want a $500 crypto loan on Aave. You might have to provide a figure like $750 of another cryptocurrency as collateral. This arrangement acts as a safety net for the lender. So, if the value of your collateral drops and it's not enough to cover your loan, the system might sell your collateral to cover the cost.
Aave Liquidity Pools
Lenders can deposit their digital assets into Aave liquidity pools. These pools then become the funds for lending. Borrowers can buy over-collateralized loans with several ERC20 tokens and stablecoins that are valued fairly by the protocol using price oracles under a common currency, typically ETH.
Lenders receive aTokens that represent their share of the funding pool. For example, if they deposit DAI, they will receive an equal number of aDAI tokens redeemable for DAI at any time. The borrowers pay interest on their loans and the Aave smart contract automatically distributes them proportionally to addresses holding aTokens.

The protocol decides lender and borrower interests algorithmically. The cost of money for borrowers depends on the available funds. The protocol raises interest as the reserve shrinks. The lenders earn a portion of the interest collected from the borrowers. The algorithm ensures an optimal earn rate while maintaining sufficient liquidity to manage withdrawals.
Interestingly, Aave isn't just about digital assets. They also have pools for real-world things like real estate, invoices for shipping, and payment advances. They've partnered with Centrifuge RWA to help regular businesses turn parts of their operations into digital tokens. These tokens work a bit like bonds and can earn people extra money. These real-world tokens can even be used as a promise to pay back loans.
In summary, Aave is all about making lending and borrowing in the digital world more accessible and efficient, and not just about cryptocurrencies, all while putting you in control of your financial choices! Something traditional banks appear less keen to do.
" Aave Liquidity Protocol: Earn interest, borrow assets, and build applications." Source: Aave
How Aave Liquidity Pools Work
The Aave liquidity pools work through an interplay between lenders, borrowers, the pool smart, and other participants facilitating the pool economy. Let’s explore the related concepts:
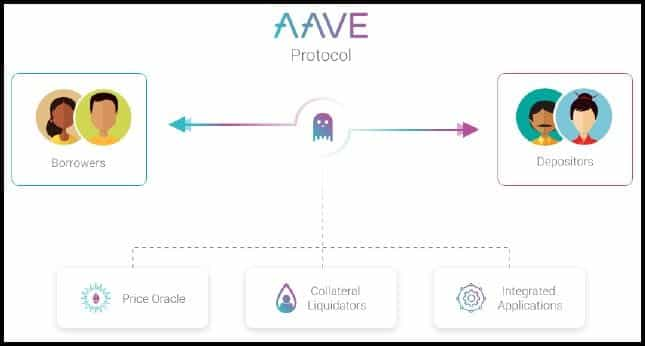
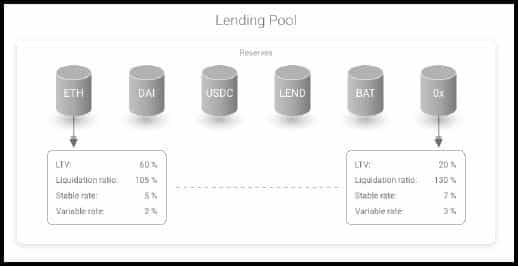
Lending Pools are central to the supply-and-demand economics of Aave. A pool is a smart contract to which lenders supply funds and the borrowers withdraw. A lending pool may comprise multiple assets (ETH, DAI, USDC, AAVE, BAT) and accept various digital assets as collateral. The Lending Pools are based on certain parameters:
Loan to Value (LTV)
The Loan-To-Value (LTV) ratio is a financial term used to describe the ratio of a loan to the value of an asset purchased. The LTV ratio determines how much a borrower can take out in loans against their collateral. It's a key metric in DeFi platforms to ensure that loans are over-collateralized, reducing the risk of loss for lenders.
Suppose you want to borrow funds using ETH as collateral on Aave, and the LTV for ETH is 50%. If you deposit 10 ETH as collateral and 1 ETH is worth $3,000, your collateral's total value is $30,000. With an LTV of 50%, you can borrow up to $15,000 worth of other assets. If the value of ETH drops, affecting the total value of your collateral, you must adjust the loan amount or add more collateral to maintain the LTV ratio and avoid liquidation.
Aave lending pools comprise multiple assets, each with separate LTVs. The LTV of the entire pool is the weighted average of the comprising LTVs, where the weight is the amount of collateral in ETH. A higher LTV means more can be borrowed against the collateral, but it also increases the risk of liquidation if asset values fall.
Liquidation Threshold
If the value of a borrower’s collateral falls during market volatility, the pool smart contract can trigger a liquidation event. This threshold, below which liquidation happens, is the liquidation threshold. Protocol participants called Collateral Liquidators receive liquidation bonus as incentive to purchase the capital.
For instance, a $100 ETH deposit in a lending pool with a liquidation ratio of 105% and LTV of 60% must maintain a collateral value above $63 ETH to prevent liquidation. If the collateral devalues, the borrower has to either pay back some loan or issue more capital to maintain the liquidation ratio.
Interest Rates
Aave offers two types of interest rates for borrowers: stable and variable. Here's how each works:
Variable Interest Rate:
This rate changes based on the supply and demand dynamics of the specific asset in the liquidity pool. If there are more deposits than borrows, the interest rate tends to decrease to encourage borrowing. Conversely, if there's more borrowing demand, the interest rate increases to incentivize deposits.
This rate is ideal for borrowers who want to take advantage of potentially lower rates and are comfortable with rate fluctuations over time.
Stable Interest Rate:
This rate is fixed for a period, offering predictability in interest payments. It's not entirely permanent but adjusts in response to extreme fluctuations in the underlying variable rate to maintain the protocol's equilibrium and stability. Borrowers who prefer stable rates seek certainty in their interest obligations, which is useful for long-term financial planning.
The stable rate is usually higher than the variable rate at any given time to compensate for the risk the protocol takes on by offering a fixed rate.
The stable interest rate is the average of the asset's last 30 days of interest rates. The interest rate history is transparent when lending or borrowing an asset on the platform. You can switch between stable and variable rates anytime (you just have to pay a small ETH gas fee).
Aave Flash Loans Explained
Flash loans are a unique feature of decentralized finance (DeFi) that doesn't have an equivalent in traditional finance. They're a novel Web3 concept that allows users to borrow assets without collateral under the condition that the loan is repaid within the same transaction block. Here's how they work in Aave:
- Web3 Native Concept: Flash loans are unique to blockchain and DeFi, enabling sophisticated financial operations that are not possible in traditional finance due to the requirement of collateral and the time taken for loan approval and disbursement.
- Atomic Transactions: A flash loan consists of multiple steps that are bundled into a single transaction. This transaction maintains atomicity, meaning all the individual operations within it either succeed together or fail together without any intermediate states.
- Arbitrage Example: Imagine a scenario where there's a price discrepancy in ETH across two platforms - it's $3100 in an Aave pool and $3000 on Sushiswap. You can capitalize on this by borrowing $3000 USDC from Aave, purchasing 1 ETH for $3000 on Sushiswap, and then selling it for $3100 in the Aave pool to repay the loan and pocket the $100 difference as profit, all within a single transaction.
- Execution and Analysis: Aave's protocol assesses the transaction to ensure that the borrowed amount can be repaid by the end of the transaction sequence. If the protocol determines that the repayment is feasible, it executes the transaction. If not, it reverses the transaction to prevent loss.
- Atomicity and Flash Nature: The requirement that all actions within a flash loan occur in the same block ensures the transaction's atomicity. This is why they're called "flash" loans—they happen almost instantaneously within a single block on the blockchain.
- Market Stability and Low Interest: Flash loans can contribute to market efficiency by enabling arbitrage opportunities that help align prices across different platforms. Since these loans exist for only a block's duration, they typically attract minimal interest, further incentivizing users to leverage them for quick financial operations.
Flash loans are a powerful tool in DeFi, offering users the ability to perform transactions that would be impossible in traditional finance, driving innovation and efficiency in the market. They have allowed cryptocurrency traders to do a whole bunch of wacky stuff, primarily yield farm. They are the key to the now famous Compound yield farming technique within InstaDapp, a DeFi protocol aggregator.
What is more is that Aave has made the underlying code to flash loans publicly available, which opens the door to many other possibilities since virtually any other Ethereum developer can implement it on their platform. This is in fact why InstaDapp is also able to offer the feature.
Aave V3 Overview
In January 2022, Aave released the technical paper for Aave V3, marking a significant step in its evolution. As Aave reached an impressive $30 billion in peak liquidity, V3 was designed to enhance essential features like aTokens and interest rate models, positioning Aave to provide a more efficient lending environment across the expanding multi-chain Web3 landscape. The four key areas of improvement are:
- Capital Efficiency: The aim is to increase the capital efficiency within the protocol, allowing lenders to generate more revenue from their deposits and enabling borrowers to loan more assets against the same collateral, all while maintaining the systemic risk of the protocol at optimal levels. This includes:
- Optimizing Borrowing Power: Adjusting risk parameters for borrowing to be less conservative, especially considering the diversity of collateral types.
- Addressing Inefficient Underlying Network: Tackling the high gas costs on the Ethereum mainnet, where a significant portion of Aave's liquidity is concentrated.
- Reducing Liquidity Segregation: Enhancing the protocol's structure to minimize isolated pools and improve overall capital efficiency.
- Protocol Safety: Implementing advanced defense mechanisms to protect against potential threats, like infinite minting or oracle manipulation, enhances the security and trustworthiness of the protocol.
- Decentralization: Modifying the governance framework to reduce gatekeeping roles, thereby providing more autonomy to various teams and projects seeking to tap into Aave's liquidity by listing their tokens, promoting a more inclusive and decentralized ecosystem.
- User Experience: Focusing on improving the user experience through the facilitation of seamless cross-chain value and liquidity transfers, making the platform more intuitive and accessible to a broader user base.
Aave V3 represents a strategic upgrade, addressing critical aspects of the protocol to ensure its competitiveness and relevance in the fast-evolving DeFi space.
What's New in Aave V3?
Aave V3 represents a set of new features and improvements to existing models that seek to improve upon the areas mentioned in the overview. The scope of this update is expansive, including new products for users to explore and extensive under-the-hood improvements that make Aave a more efficient lending protocol. Here's an summary of the most important upgrades you should know about:
Portal
Aave is active in an impressive selection of markets:
- Ethereum: The largest market on the Aave protocol.
- Optimism: A fast, secure, and simple" EVM equivalent rollup chain."
- Metis: A Layer 2, EVM-compatible scaling solution using optimistic rollup technology.
- Arbitrum: This network has the security of the Ethereum network but with faster speeds.
- AMM: “Reduced volatility from supplying assets and earn trading fees from the market.”
- Polygon: Lower fees and quicker transactions mean using Aave on Polygon is ideal for high-volume transactions.
- Avalanche: Known for cheap, fast transactions, Avalanche offers AVAX rewards for supplying liquidity or borrowing.
- Solana: A non-EVM smart contract layer-1 famous for fast transactions and economical fees.
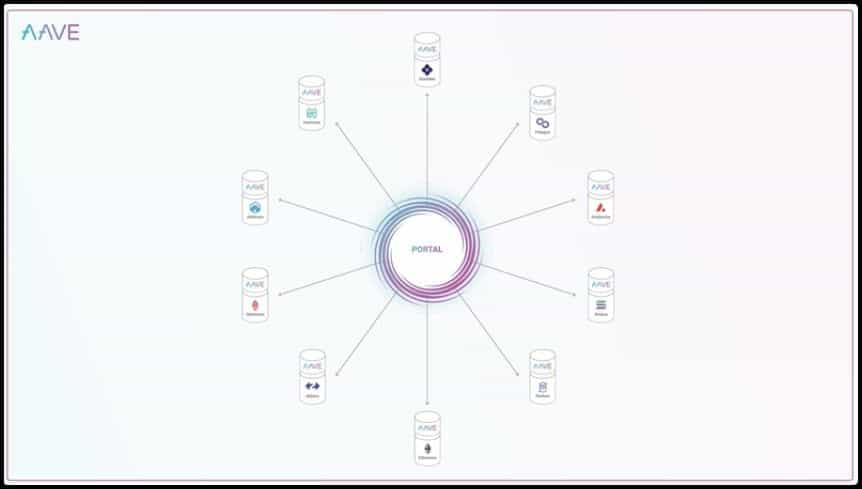
The Portal allows the canonical use of governance-backed bridges like Connext and Hop Protocol to bridge tokens across pools operating in different networks. Therefore, the Portal opens up scenarios where a user could supply collateral in the Ethereum network and use it to borrow funds on another network, say Arbitrum or Polygon. The Portal burns the aTokens on the source chain and simultaneously mints an equivalent amount in the destination chain, allowing seamless cross-chain liquidity flow.
Efficiency Mode (eMode)
The new efficiency mode is a new introduction to the Aave protocol that seeks to optimize the conservative risk parameters of the protocol we discussed earlier. Consider a scenario where the borrower collateralized its loan position with several different but correlated digital assets. For instance, your collateral is spread in different stablecoins (USDC, DAI, USDT) or similar tokens (ETH, stETH, alETH). These tokens are technically different, but their correlation to a common underlying means their volatility is predictable.
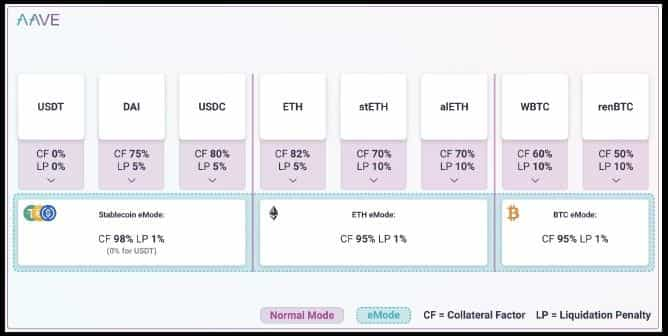
In such cases, eMode overrides Aave's standard methodology for LTV, interest and liquidation calculation with the efficiency mode, letting users borrow more capital from the same collateral. The illustration above shows the eMode offering 23% more capital efficiency in the stablecoin eMode.
GHO Stablecoin
In July 2023, AAVE launched the algorithmic GHO stablecoin on the Ethereum mainnet.
GHO is a fully backed, multi-collateral, transparent, decentralized stablecoin native to Aave. Suppliers and borrowers can mint the GHO coin by using assets they supplied as collateral to V3 on Ethereum markets, and they continue earning interest on underlying assets. Borrowing GHO is similar to other assets across the different Aave markets, but repaid interest goes to the Aave DAO rather than the asset supplier.
GHO has been described as a “not-so-stablecoin" because stablecoins are pegged to the U.S. dollar, meaning their price is always $1. That's not the case with GHO. While it has come close, the coin has failed to reach the coveted $1 price for nearly all of its life. At the time of writing, one GHO was worth $0.97.
In November 2023, GHO reached its minting cap.
Other Improvements
Aave V3 further comprises several nuanced improvements that prove essential in typical scenarios:
- Isolation Mode: This mode allows Aave to approve new tokens for use as collateral in a controlled setting, imposing a debt ceiling and limiting access to the protocol's liquidity to stablecoins.
- Siloed Borrowing: If Aave governance configures an asset as siloed, borrowers are restricted to borrowing that asset individually, limiting them from including it in a basket of borrowed assets.
- Supply and Borrow Caps: Aave Governance can appoint RISK_ADMIN and POOL_ADMIN, who can configure the borrow and supply Caps of the individual reserves.
- Repaying with aTokens: V3 allows the user to repay with aTokens if the underlying borrowed asset is locked in the Aave liquidity pool.
- Configurable Rewards: Aave V3 offers the option of multiple rewards per token. Now, an asset listing can enable additional incentive rewards denominated in protocol tokens. V3 also allows users to claim rewards to another account as well as themselves and to claim multiple types of rewards per asset in a single TX.
- Migration Tool: Aave facilitates the migration of positions from V2 to V3 via a new migration tool that summarizes risk parameters in both situations so that users can decide which model works best for them.
AAVE Governance Tokens
Aave began migrating LEND tokens to AAVE in late 2020 at a rate of 100 LEND tokens for 1 AAVE, dropping the total supply to 18 million AAVE tokens. At the same time, Aave introduced a game studio for blockchain games, a trading desk for the management of large trades and a payment handling system.
Governance in Aave is implemented on two levels:
- Aave Protocol governance facilitates protocol-level decision-making involving version upgrades, creating new pools, etc. The vote is measured in AAVE tokens.
- Lending pool governance facilitates pool-specific decision-making. The vote is measured in aTokens of a specific lending pool.
AAVE is the governance token for the Aave protocol. One AAVE token equals one vote, so the more tokens a user holds, the more voting power they have. AAVE can also be used as collateral for borrowing. In addition, you can receive discounts and bypass borrowing fees if you directly borrow AAVE.
Where to Buy AAVE Tokens
AAVE tokens are available on some of the leading, established cryptocurrency exchanges, such as the following:
You can store your AAVE tokens in a selection of crypto wallets, such as Trust Wallet, MetaMask and the Ledger hardware wallet.
Aave Community And Security
Aave Grants DAO
The Aave Grants DAO is a program led by the community for funding ideas from Aave holders. The focus is to empower a “wider network of community developers.”
Aave Security
Some of the leading security firms audit the Aave network: -
- Trail of Bits
- Certora
- OpenZeppelin
- SigmaPrime
- PeckShield
- ABDK
Aave has a Safety Module, a safe backstop of $283,513,952 in case of protocol insolvency.
Aave also has a generous bug bounty for its community to identify potential vulnerabilities or bugs. Depending on the evaluation of the severity of the issue exposed, Aave will pay a reward of up to $250,000.
"Bug Bounty: We want the Aave protocol to be the best it can be, so we're calling on our community to help us find any bugs or vulnerabilities." Source: Aave
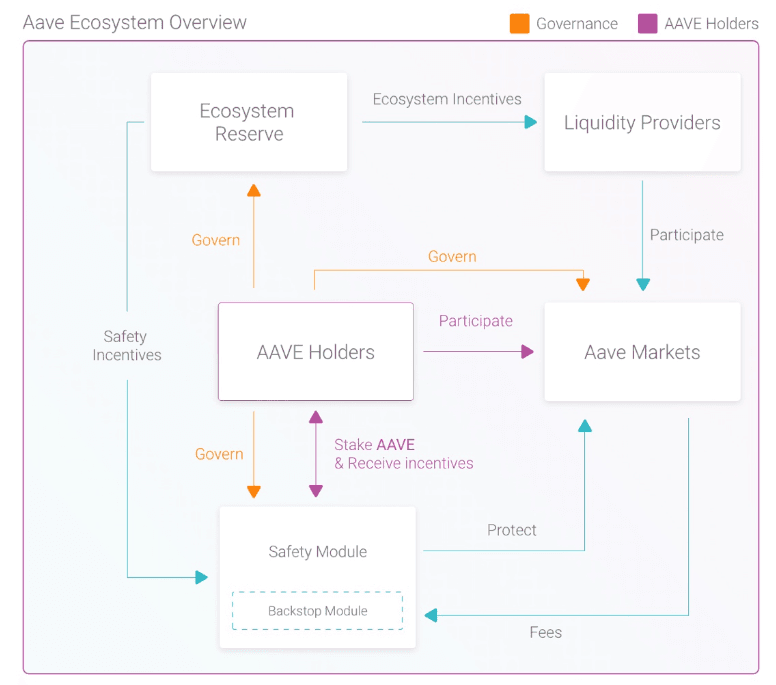
The Aave Community Treasury
The Aave treasury comprises ecosystem reserve (AAVE tokens), and in addition, treasury collectors earn a percentage of fees from the following: -
- Reserve Factor: Interest paid by borrowers.
- Instant Liquidity Fees from transactions.
- Liquidation Fees: (not yet active August 2023): Collateral liquidation bonus.
- Portal Fees: (not yet active August 2023) paid by “bridging protocols to reback assets.”
Aave Community
Aave has over 29,000 Discord members and over 572k Twitter followers in April 2024.
"Governed by the community: Aave is a fully decentralized, community governed protocol with 155,881 token holders."
Aave vs. Compound
Aave and Compound are both overcollateralized cryptocurrency lending protocols and operate similarly—both protocols pool lenders' assets into liquidity pools, which fund loans.
They both have a governance token and are two of the largest protocols in DeFi in terms of "assets under management" (AUM). However, Compound is less complex but does not offer as many features as Aave.
Aave offers stable Interest rates, but Compound does not. Aave allows you to switch between stable and variable interest rates; Compound does not. Aave has Flash Loans, but Compound does not.
On paper, Aave seems objectively better than Compound as a cryptocurrency lending protocol. However, there are two advantages Compound has over Aave. The first is that it is more user-friendly.
Not having as many features makes it easier for new users to understand and navigate. Compound incentivizes users to participate in the protocol by providing lenders and borrowers with a small fraction of COMP tokens every few seconds.
In summary, the key differences between AAVE and Compound.
- Native token: AAVE is a native governance token for Aave, for token holders to vote on the direction of the protocol. COMP is the governance token for Compound protocol.
- Different Ways of Determining Interest Rates: Aave uses the Utilisation rate of crypto assets to determine interest rates, whereas Compound uses algorithms based on supply and demand for each asset. Aave supports various crypto assets for borrowing, and Compound uses cTokens for lending and borrowing.
- Debt Closure if Under-Collateralized: If the collateral for borrowing falls lower than the borrowed amount, Aave rewards liquidators to close debt positions, and Compound's Comptroller does the same.
Aave New Developments
Aave (AAVE) companies added a new open governance model (LIPS) and recently launched Lens Protocol, an NFT-powered, decentralized social media platform. LIPS (Lens Improvement Proposals) uses elements from Ethereum and Aave improvement proposals models.
Lens raised $15 million to help build and expand the new platform. The functionality will undoubtedly be unique for a decentralized platform, as users can block users on-chain, as you can on Facebook or other centralized social media channels.
Lens built the protocol on top of Polygon, an Ethereum scaling solution. Lens community members can tokenize social data with NFTs and smart contracts and have the power to propose improvements to the protocol.
"Designed to be interoperable, Lens can be integrated with other Web3 applications. This allows creators to build their own custom social media experiences." Source: Lens
Aave founder Stani Kulechov stated that the "Lens Protocol V2 takes decentralized social media and monetization opportunities to a new level."
The new platform should attract content creators, developers and interested users in the decentralized social media aspect. It will be interesting to see how Lens shapes up over time. With Elon rolling out X, amid the debacle argument that Meta owns the "name", most of us are tired of the big tech, centralized social media companies and eager to try something new.
Aave Review: Conclusion
Aave is a promising project and a behemoth in the DeFi space. Compared to DeFi lending protocols, it offers an arsenal of features, assets, and development tools to allow others to implement these same features into their own DeFi projects.
One of the unique features of Aave is the Flash Loans. Proponents of Flash Loans argue (and rightfully so) that it allows people without absolutely no assets to try their hand at quickly turning a profit in DeFi.
Perhaps the most famous case of this involves a “hacker” who used a Flash Loan with $10 USD to turn a profit of nearly $400,000 USD using arbitrage. Doing something like this without incurring a substantial amount of debt or risk is impossible in classical finance and opens a whole new world of potential.

In April 2023, according to several reputable sources, a Flash loan exploiter got away with $10 million in stablecoins with Yearn Finance and Aave.
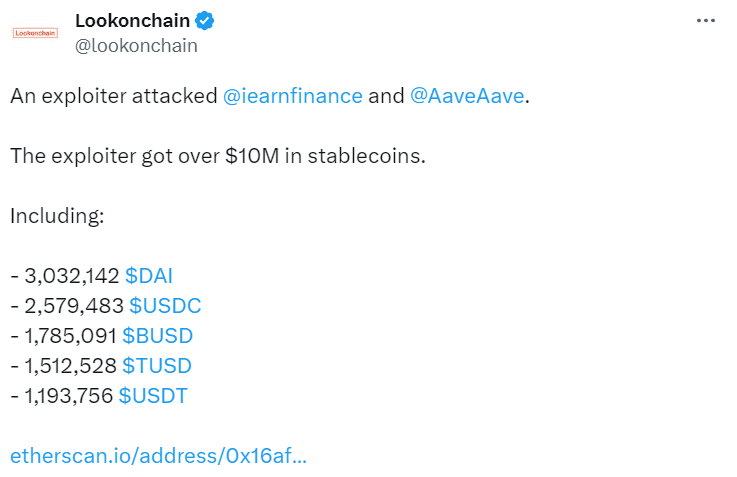
Peckshield, a leading blockchain security company, one of Aave's security auditors, reported that the origin of the exploit was not related to Aave. Rather, it was due to a misconfigured uYSDT. The consensus seems to be that it did not affect V2 or V3.
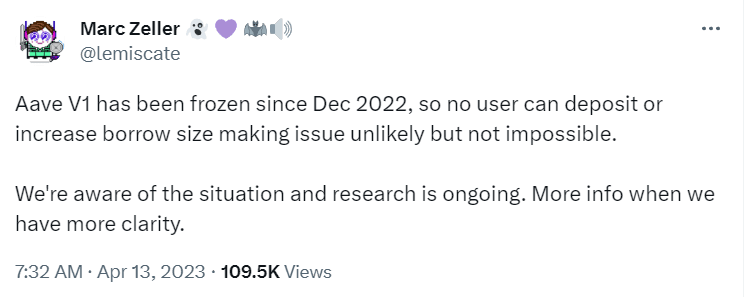
Marc Zeller, founder of ACI, a blockchain consulting company, has worked with Aave since 2019.
Furthermore, Aave's founder Stani Kulechov seems to have a firm grasp of what DeFi needs to reach mainstream adoption. In an interview, he noted that it all boils down to quantifying risk and making it transparent to investors, especially institutional investors.
The fear of risk is why people turn away from cryptocurrency, and the reality is that it is a risky and volatile asset class. However, Kulechov believes it's vital to help people understand the risks, which could bring the wave of adoption the entire crypto space has been waiting for.
Finally, Kulechov noted the elephant in the room. How do you incentivize and operate services such as customer support without a centralized structure? It's a constant puzzle for a decentralized industry. However, it seems to be the driving force behind the Aave protocol, and we will undoubtedly see more evidence of this mission over time.
Although Aave has plenty of documentation on the internet, it would be beneficial to add the roadmap to the main website and have more synergy between shared information.
Frequently Asked Questions
Aave has a lot going for it as a major DeFi protocol. Founded in 2017, the Aave team have worked hard to differentiate itself from the market. AAVE is a well-established token and has done well, once reaching over $666 all-time high. However, as the bull market picks back up in 2024, all of DeFi is in price discovery mode.
Aave minimizes risk as much as possible, but nothing is entirely risk-free. There are two potential risks: -
- A bug or hacker gets into a smart contract code
- Liquidation risk
- Impermanent Loss
The Aave protocol code is open-source, public, and audited by multiple security companies. In addition, Aave operates a bug bounty program and Safety Module, a safe backstop of $283,513,952 in case of protocol insolvency.
One of the potential disadvantages of Aave is the risk of over-collateralization. When someone borrows, they must contribute more value than the loan. For example, if you borrow $100 of assets, you may need to provide $150 of assets for collateral.
There are also criticisms against the centralization of wealth in the top 10% of Aave holders.
If you deposit assets in the liquidity pools, you can earn from the distributed interest collected from borrowers.
Aave is trying to solve some of the most frustrating issues in traditional lending services. The main objective is to help users transition from centralized to decentralized finance services.
Disclaimer: These are the writer’s opinions and should not be considered investment advice. Readers should do their own research.


