QuarkChain (QKC) is trying to solve one of the most pertinent issues that cryptocurrencies currently face, that of the blockchain trilemma.
The project has been gaining quite a bit of traction ever since their successful ICO earlier this year. People were intrigued by the promise 1m transactions per second built on a two layered blockchain that will implement sharding.
However, are these just mere promises in another whitepaper?
In this QuarkChain review, we will take a deep dive into the project by analysing not only at the proposed technology but also at the practicality of it. We will also look into the team members, adoption, roadmap and long term QKC token prospects.
With that being said, let's jump right into the need for a QuarkChain like solution.
What is QuarkChain?
QuarkChain is a decentralized blockchain that is also permission-less and secure, but most importantly it is scalable. The QuarkChain team has as one of its major goals to utilize sharding technology and deliver in excess of 1 million transactions per second.
It is looking to become the blockchain for high capacity throughput, delivering a solution that is secure and fast enough for widely used decentralized applications (dApps).
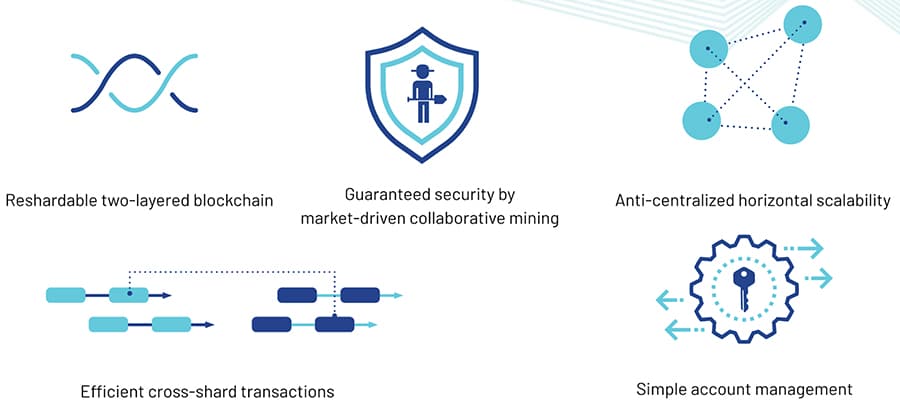 QuarkChain Main Features. Source: medium
QuarkChain Main Features. Source: mediumScalability has been one of the biggest hurdles faced by blockchains in 2018, and QuarkChain was created specifically to resolve scalability issues faced by blockchains. This has become an urgent issue for the industry, and is one that the team feels simply cannot wait any longer.
They have embarked on providing a solution that may be different from those put forward previously, but could also be the one that actually works best. They’re not afraid of needing a hard fork if that’s what it takes to succeed.
QuarkChain’s Scalability
QuarkChain’s sharding technology will enable up to 1 million transactions per second. As a comparison, Bitcoin can only deliver 4 transactions per second, while Ethereum delivers 10 transactions per second. Even the Visa network is only capable of delivering 45,000 transactions per second.
If QuarkChain can meet the goal of 1 million transactions per second it will be by far the fastest network on the planet. This could see it overtaking Ethereum as dApp developers switch to QuarkChain to support increased usage.
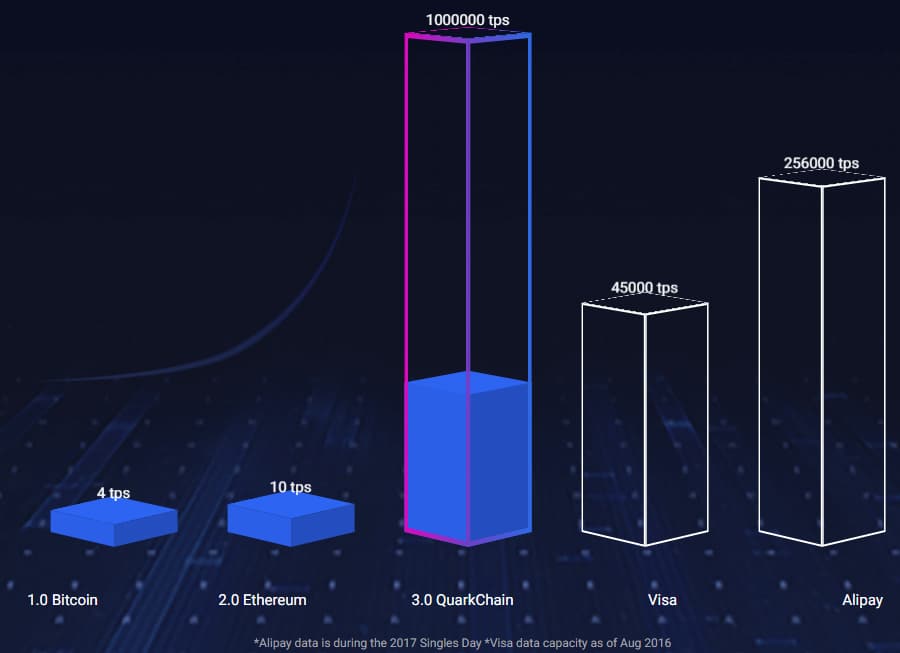 QuarkChain Transaction Speeds compared to other Chains. Source: Hackernoon
QuarkChain Transaction Speeds compared to other Chains. Source: HackernoonSharding is the primary reason that QuarkChain can deliver such a fast network, but since it is a blockchain it still brings decentralization and security. And the development team have experience at major tech companies, giving them the ability to create and deliver a large-scale distributed system. It also gives the team the knowledge needed to create scalability by extending their knowledge of centralized systems to the decentralized QuarkChain system.
QuarkChain Beyond High TPS
QuarkChain has pointed out that there are other projects that have transaction per second rates that are greater than the Visa 65k per second, but then go on to point out that TPS isn’t the only metric that needs to be considered in a network.
The QuarkChain team specifically mentions Alipay, which has reached 200,000 transactions per second, but has done so by sacrificing decentralization and security. QuarkChain is aiming for scalability that includes decentralization and security, making it a superior network, if the team is successful.
Why QuarkChain is Different
Besides its focus on fast throughput, there are other features of the QuarkChain network that make it different from other decentralized blockchain projects.
One of these features is the incentivization of weak miners to participate in the network without joining a mining pool. This incentive is based on game theory and works by giving miners an incentive for distributing hash power equally among the shards. This also increases decentralization.
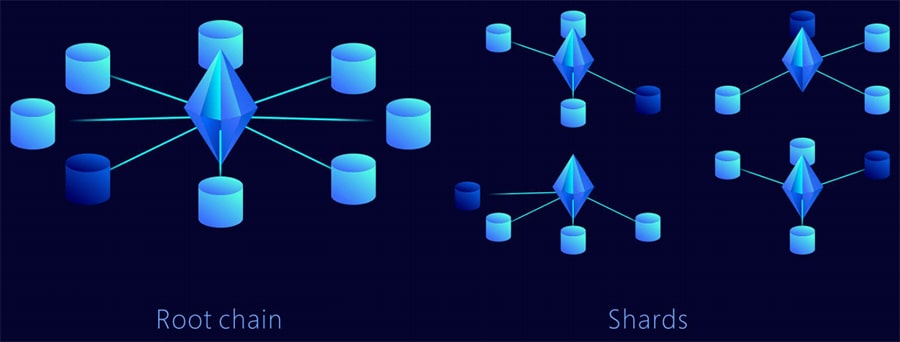 Illustration of Collaberative Mining at QuarkChain. Source:Whitepaper
Illustration of Collaberative Mining at QuarkChain. Source:WhitepaperAnother way that decentralization is encouraged is through the use of multiple cheap nodes which are joined in a cluster to make a super-full node. By using cheap nodes in clusters to create super-full nodes, the project avoids the high expenses that super-full nodes are subject to in high transaction per second environments.
The network increases security by providing every transaction with the protection of 50% of the network hash power. By combining this protection with network decentralization it become nearly impossible for a bad actor to conduct a double-spending attack.
The structure of QuarkChain is reliant on two layers. The first layer consists of sharding blockchains, called shards, and the second layer is the root blockchain which is used to confirm shards blocks and provide security for the entire network.
 Structure of Quarkchain Network. Source: Whitepaper
Structure of Quarkchain Network. Source: WhitepaperQuarkChain has also built-in support for cross-shard transactions, and was built so that one account can be used for all the shards. It was also designed so that a single smart wallet is used to hold all the cryptocurrencies that can be associated with various shards.
The benefit of the cross-shard transactions is that they can be issued anytime, and can be confirmed within minutes. The cross-shard transaction throughput also increases linearly as the number of total shards increases, providing scalability.
How to get Involved with QuarkChain
QuarkChain has offered several ways for the community to get involved in the project. The testnet for the project was only launched in May 2018, but prior to the launch they actively recruited 100 volunteers from the community to act as beta testers. It also welcomes anyone with blockchain development experience and a strong technical background to get involved in the project.
On September 17, 2018 the team made their code open source on Github so that anyone can inspect it. Further, they are running a developers contest to see who can build a QuarkChain testnet by running their own nodes/clusters and achieve the greatest transactions per second utilizing a provided load test. The winner will receive 1 BTC, with additional prizes for places 2 through 10.
Currently the peak testnet performance is 14,755.25 transactions per second.
QuarkChain Tokens (QKC)
QuarkChain tokens have the ticker symbol QKC and they are currently ERC-20 compatible tokens on the Ethereum blockchain. Once the QuarkChain mainnet is launched these will be converted to native tokens through a premine, and in the future miners will produce QKC tokens.
QuarkChain held their ICO in June 2018, raising $20 million at a token price of $0.0197. There was a total of 10 billion tokens created, with 20% allocated to the ICO sale. The rest of the tokens were allocated as follows: 15% to the development team, 5% to the project advisors, and 15% for the QuarkChain foundation.
The remaining 45% are to be allocated for marketing, mining and to the community. It’s already been noted by the QuarkChain team that mining is likely to create some inflation in the future.
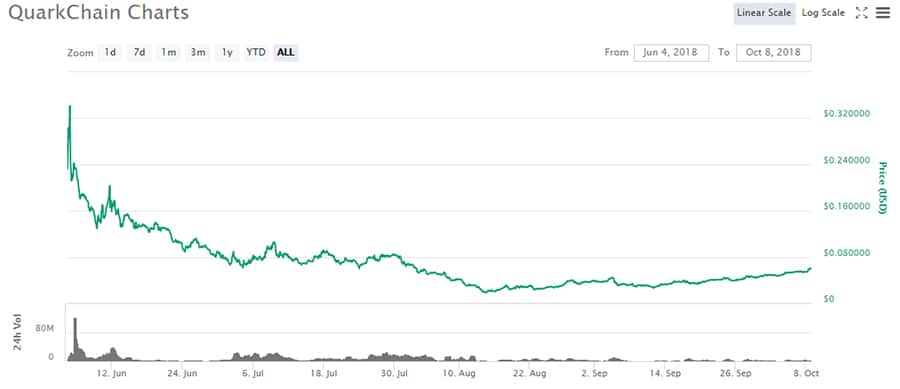 QKC Price Performance since ICO. Image Source: Coinmarketcap
QKC Price Performance since ICO. Image Source: CoinmarketcapThe price of QKC jumped to $0.268 just one day after the ICO, but by June 9, it declined by more than half to $0.129677. After a quick pop higher in June it steadily declined to a low of $0.021378 by August 14, but has been recovering slowly, but surely since then and as of October 8, 2018 is trading at $0.0594, which is still a very nice return from the June 3 ICO price.
If you are interested in buying some QKC tokens yourself they are available at Binance for either BTC or ETH. There are also a number of smaller exchanges that offer QKC, such as Gate.io and KuCoin, but you still cannot purchase them with fiat currency.
Register at Binance and Buy QKC Tokens
Since QKC is an ERC-20 compatible token it can be stored in any ERC-20 compatible wallet such as MyEtherWallet or MyCrypto, MetaMask and others. The most secure method of storage is in a hardware wallet though.
dApps on QuarkChain
One of the key aspects of QuarkChain is its support for dApps. It is open to a large number of dApps, and is especially good for those that require high throughput. This includes dApps related to gaming, artificial intelligence, peer-to-peer economies, Internet of Things, big data and even advertising.
QuickChain could have been an excellent solution during the CryptoKitties excitement, and it feels it can provide an excellent home for a number of dApps that have been on hold while waiting for a blockchain that can provide the scalability necessary for them to deliver their full potential.
QuarkChain Team & Advisors
QuarkChain seems to have some pretty experienced team members and a strong advisor pool. For example, Qi Zhou (Founder) is a software engineer who used to work at Google and has over 15 years of experience. He also has a doctorate from the Georgia Institute of Technology.
 Quarkchain Team Members
Quarkchain Team MembersJoining him is Zhaoguang Wang who is also a software engineer and is an expert in distributed systems. He used to work at Facebook and Google and has a Msc in Computer science from the university of Michigan. There are also a number of other scientists and researchers who complete the team.
On the advisor side they have, among others, Paul Veradittakit who is a partner at Pantera Capital and Bill Moore who is an engineer at Sun Microsystems.
QuarkChain Roadmap
The bulk of work for QuarkChain began midway through 2017 as the development team began to research issues relating to blockchain scalability. By the end of 2017 the team had drafted their whitepaper, and after editing and revisions that was released in February 2018. At the same time they completed verification code 0.1. Just one month later the 0.1 versions of the testnet and wallet were released.
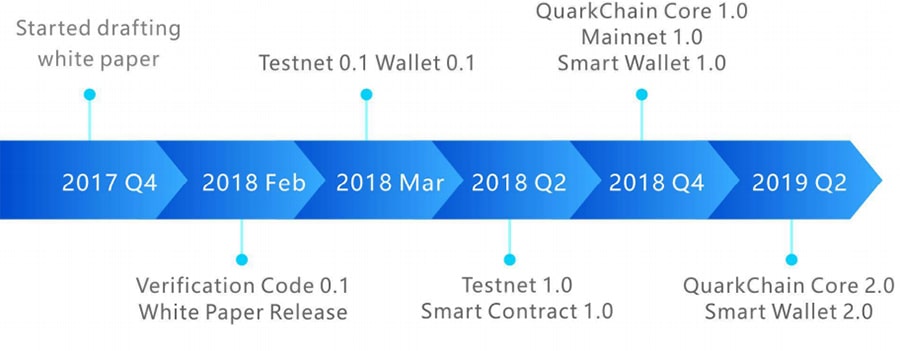 Quarkchain Roadmap. Source: Whitepaper
Quarkchain Roadmap. Source: WhitepaperBy the second quarter of 2018 the team was working on testnet 1.0 and that was released in July 2018. They were also working on smart contract 0.1. The roadmap claims that QuarkChain Core 1.0, mainnet 1.0 and SmartWallet 1.0 will all be released before the end of 2018. By the second quarter of 2019 it is planned to have the QuarkChain Core and SmartWallet both at their 2.0 versions.
Conclusion
2018 has seen a massive focus on scalability issues from across the blockchain ecosystem. While there are several other projects looking to solve the scalability problem, the QuarkChain sharding solution is on track to create a blockchain free of scalability issues.
If they accomplish this it would be a great breakthrough for blockchain technology, since many of the planned applications using blockchain technology are hampered by issues of scalability.
It’s true that the project is still very much in development, but they have made great progress, and have been hitting their projected completion dates with regularity. This leads to confidence in the team and the project, and if the mainnet launches before the end of 2018 this could become one of the most talked about blockchain projects in 2019.