Hedera Hashgraph: Next Generation DLT Challenging Blockchains
Hedera Hashgraph is a project that has got the whole crypto community fired up. Boasting network stats like 10,000 transactions per second, its no wonder why.
The Hashgraph is a completely new technology that has been developed for industry clients. However, the project has launched an open source version of their technology which many in the industry think could challenge established blockchains.
However, is it really all that it is being talked up to be?
In this Hedera Hashgraph review I will attempt to answer that. I will also analyse the long term use cases and adoption potential of the HBAR coin.
What is Hedera Hashgraph?
The Hashgraph is what Hedera calls its new form of distributed ledger technology (DLT). This DLT technology is when a network of computers communicate with one another in order to reach an agreement over something, known as consensus. In the case of Hedera, the agreement is whether transactions are valid, and the network is decentralized to maintain security and fairness.
This all probably sounds familiar if you know anything at all about blockchain technology because blockchains are another form of distributed ledger technology.
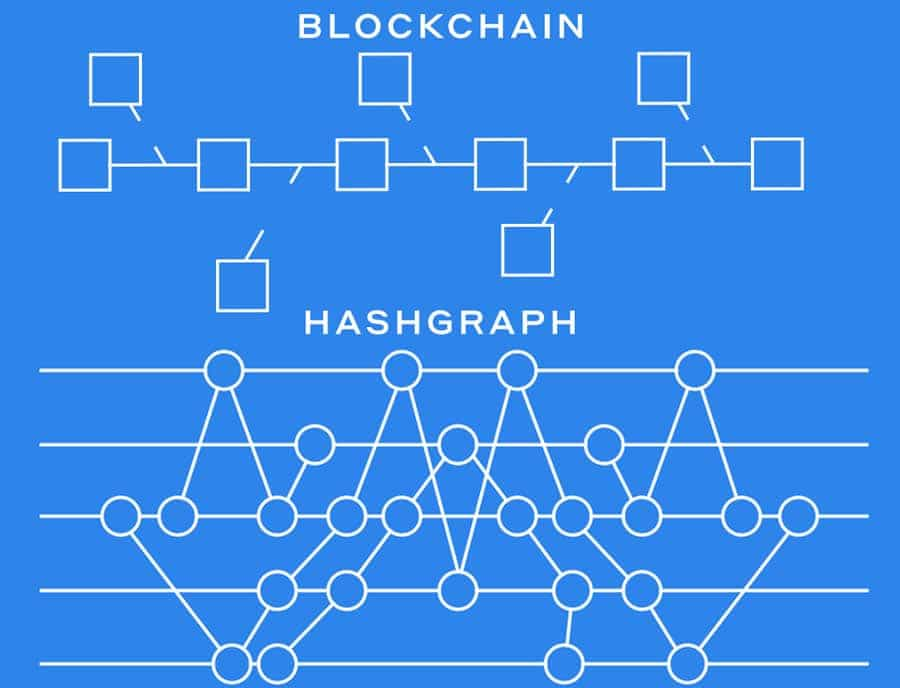
Hedera Hashgraph is different however as it uses something called directed acyclic graph (DAG) technology. The consensus algorithm it uses includes something called Virtual Voting, as well as a Gossip to Gossip protocol.
The whitepaper also claims Hashgraph has “guaranteed Byzantine fault tolerance,” making it more secure, faster, and fairer than other consensus mechanisms. This allows Hashgraph to be scalable, efficient and more secure, all of which are improvements over blockchain solutions.
Hedera Hashgraph Platform
Hedera Hashgraph was created by Dr. Leemon Baird and was launched by Swirlds, a company he co-founded, in 2016. It is a public ledger using the patented Hashgraph technology and is described as an asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (aBFT) consensus algorithm capable of securing the platform against attacks.
The Hadera Hashgraph platform is amazingly fast and is also secure and fair, plus it requires very little in the way of computational resources to keep the network secure. With Hadera, anyone is capable of running a node, creating a dApp, or use the service free of the need to license the technology.

The only thing held apart is the Hashgraph technology, which was patented by Swirlds to avoid competing ledgers using Hashgraph technology from springing up.
The Hashgraph platform was created for enterprise applications, and Hedera was built on top of the Hashgraph. The mainnet beta launch of Hedera Hashgraph was completed in August 2019.
This allows for the three main services provided by Hedera, namely the HBAR cryptocurrency meant to support micro-transactions, a distributed file system, and support for solidity smart contracts.
Problems Solved by Hedera Hashgraph
There are five problems that are being targeted by Hedera and the Hashgraph attempts to solve. By solving these problems Hedera believes it can foster mainstream adoption of distributed ledger technology. Here are those five problems:
Performance
Hedera claims to be extremely fast, and indeed it can handle more than 10,000 transactions per second, with consensus reached within 3-5 seconds, with finality.
In the past, Hedera testnets have been able to achieve a throughput of 50,000 transactions per second, and in one test where there was a geographical constraint of just 1 continent, the platform was able to achieve speeds of 500,000 transactions per second.
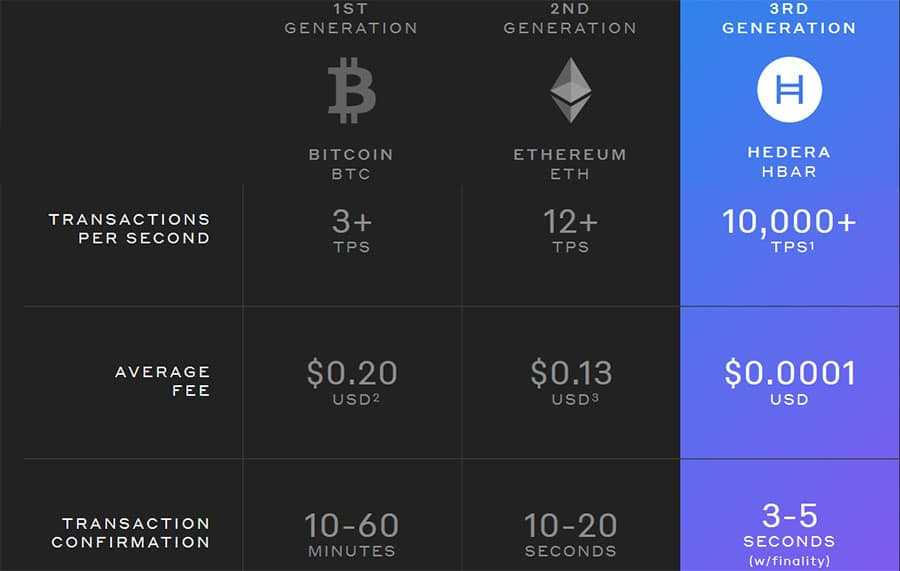
So really Hedera’s platform seems to be limited only by network bandwidth. Other networks already pale in comparison to the speeds achieved by Hedera. For example, Bitcoin has speeds of just 7 transactions per second, and even the Visa network only achieves speeds of 2,000 transactions per second.
Security
Hashgraph uses asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance (aBFT) as its consensus algorithm, and this algorithm is considered to be one of the most secure ways of providing consensus.
In using aBFT Hedera makes it impossible for any member to halt community consensus, or from changing records after consensus has been reached. The network will be able to tolerate faulty nodes, as long as fewer than 1/3 of the nodes are attackers.
Once the network reaches consensus it is known by the community immediately in real-time, and this assures that the consensus cannot be compromised. This means aBFT gives Hedera protection from malicious nodes and DDoS attacks, even if some of the network nodes are shut down or compromised.
Hashgraph is also more secure than blockchain technology due to the sense of finality provided when consensus is reached. It also addresses concerns of fairness by using Consensus Time Stamping to achieve Mathematically Proven Fairness through a democratic voting process. In this case, there are three aspects to fairness:
- Fair Access where it’s not possible for any individual to manipulate the flow of transactions, or for any node to lie about transactions.
- Fair Timestamps which reflect the true time in which a transaction has been broadcast to the majority of the network.
- Fair Ordering is achieved through the use of the fair timestamp assignments.
Governance
Hadera Hashgraph comes with two governance models that have been defined in its whitepaper. The first of these is the Council Government Model, which is the overall governing body of Hadera that upholds the decentralization, trustworthiness, and stability of the network.
This council is comprised of 39 organizations which have been determined to be reputable, and which are spread across the globe on 5 continents. Each council member is limited to two consecutive three-year terms.

This setup prevents too much power from being held by a single person or organization. The second governance model is the Consensus Model which allows anyone who wishes to run a node to do so.
With the consensus model, anyone can run a node, help maintain consensus, and be rewarded for their effort. The team expects the number of nodes to grow very quickly, improving the decentralization of Hedera Hashgraph substantially.
Stability
Hedera Hashgraph has said it will never fork as the platform is kept sable with legal and technical controls that prohibit forking. That will avoid any competing platforms being created, which helps avoid confusion and uncertainty.
There are two capabilities created by the technical controls. The first is that the pedigree of the Hashgraph can always be verified by the software client through a shared state mechanism. This shared state consists of all nodes providing verified information consisting of the consensus state of the entire network.
In such a shared state it’s impossible for a bad actor to compromise the network, and it also prevents any of the nodes from forking or making changes and then pushing them to the entire network as valid.

The second capability ensures any software changes made by the governing body are guaranteed to be legitimate as they are automatically updated and specified across the network.
In addition to the technical controls, there are legal controls to avoid any fork occurring and creating a competing platform. While it’s true that the codebase of Hedera Hashgraph is open source, it isn’t possible to make updates in any way other than through the Governing Council.
Patenting the Hashgraph technology makes it impossible for another team to create a platform using the technology unless they acquire a license from Swirld.
Regulatory Compliance
Hedera has enabled KYC/AML compliance through an included, optional identity mechanism. Dubbed the Opt-in Escrowed Identity System, it allows verified identities to be bound to otherwise anonymous wallets.
This feature makes it easier for Hedera to realize mass adoption as governments continue adding regulations to the cryptocurrency landscape.
Hashgraph Consensus Algorithm
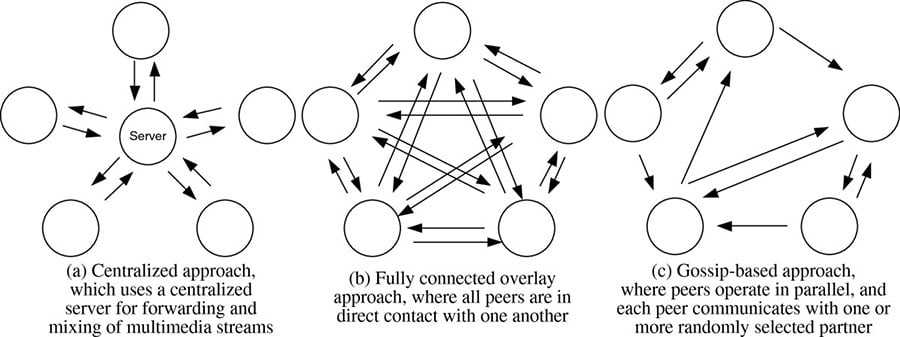
Hedera Hashgraph uses a consensus algorithm that is based on Virtual Voting and the Gossip Protocol.
The Gossip Protocol is a method for spreading information across a network in a quick and efficient manner. Using the Gossip Protocol a node can randomly choose another node it is already acquainted with and exchange all the information it has with that node. The process spreads across the entire network and increases exponentially until the entire network is aware of all available information.
In addition, instead of simply gossiping only a transaction the Gossip Protocol also allows for “gossip about gossip”, which allows for historical information to gossip across the network.
This means that nodes with slightly different information near the top of the chain can quickly come to consensus by continuously gossiping with each other. Eventually, the events converge and members lower down the chain will share the same events. This process allows the network to scale infinitely while ensuring consistency and optimizing communication across the network.
Virtual voting on Hashgraph is based on the concept of voting but is a more sophisticated method of voting that achieves strong guarantees with efficiency. With Virtual Voting, the network can run a voting algorithm without actually sending any voting messages.
This is done because the Gossip Protocol allows each node in the network to keep a full copy of the Hashgraph, complete with the history of every transaction. This feature means the nodes can “calculate a total order on the events according to any deterministic function of that hashgraph” and get the same answers.
This allows nodes to reach consensus on the validity of any transactions so long as it knows the majority of the network witnessed the transaction.
The Hedera Hashgraph algorithm is unique among distributed ledgers, and it benefits from using very little bandwidth, as well as providing exceptional honesty and transparency among the network nodes.
Hedera Team
The Hedera Hashgraph team is comprised of highly skilled and experienced professionals who bring a wealth of knowledge about blockchain, technology, and business to the project.
The Chief Scientist and co-founder of the project is Dr. Leemon Baird. Dr. Baird is the inventor of the Hashgraph algorithm. He brings more than 20 years of technology and startup experience to the project and has previously been a Professor of Computer Science at the U.S. Air Force Academy.
He also holds the position of senior scientist at a number of labs. He has been a founder or co-founder for several startup companies, including two that were in the identity field. Dr. Baird received his Ph.D. in Computer Science from Carnegie Mellon University and has acquired several patents in the fields of computer security and machine learning.

The second co-founder and the CEO of Hedera is Mance Harmon. Harmon is an experienced entrepreneur and has over 20 years as a technology executive working for multi-national corporations, high-tech startups, and government agencies.
Prior to working at Hedera, he was a founder at two tech startups, as well as a senior executive at several companies. He has been involved in cybersecurity and machine learning and received his MS in Computer Science from the University of Massachusetts.
In addition to the small and talented team working on Hedera Hashgraph, the project also has a large and diverse number of investors, partners, incubators, and accelerators.
The HBAR Coin
HBAR is the native cryptocurrency that powers the Hedera public network. It is a utility "token" which will be used for powering the decentralised applications, building Peer-to-Peer payment business models and to protect the network from any malicious actors.
When it comes to running decentralised applications, HBARs are used to pay for the computational power required to run a smart contract as well as to store file or transfer some cryptocurrency. It functions much the same way that Gas does on platforms such as Ethereum's or Neo's.
For protection, HBARs are staked or proxy staked to a network node. This means that voting power is weighted according to how much each of the members holds in HBARs. Similar to other Proof of Stake protocols, by requiring a monetary commitment, Hedera forces honest behavior from the network nodes.
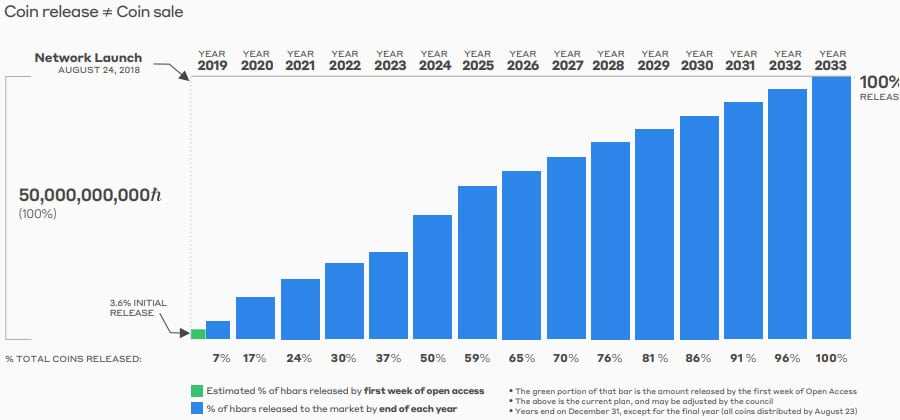
When it comes to the economics, there is a total supply of over 50 billion HBAR coins. The initial release of the coins on network launch was only 3.6%. However, the outstanding supply will increase per year according to a coin release schedule.
The slow release of the coins is intended to further provide for the stable and orderly growth of the platform so that it can reach the required scale without sacrificing any of the safety required to make the network fully trustworthy.
Price Performance
The HBAR token has only been released along with the mainnet beta of the Hedera Hashgraph platform on September 16, 2019. Prior to that, there was an ICO in August 2018 for accredited investors, as well as 2 more rounds of funding that brought the total raised to $124 million.
The August 2018 ICO price was $0.12 per token and the opening price for the HBAR token was $0.416009, however, by the end of the first trading session, the price had dropped to $0.090177.
Price has dropped even further in the following month, hitting its all-time low of $0.025871 on September 25, and as of October 14, 2019 HBAR is trading for $0.035864.
Buying & Storing HBAR
With less than a month since the token was released, it is only available at six different exchanges. Of course, some of those are among the largest exchanges. For example, the greatest trading volume is on Binance with OKEx coming in at a close second. You can also purchase tokens at Upbit, Bittrex, Liquid, and HitBTC.
When it comes to coin liquidity, it appears that most of the volume for HBARs is taking place on Binance and OkEX. Taking a look into the individual order books, they appear to be pretty deep and there is strong turnover across the HBAR / BTC, USDT and ETH markets.

Once you have got your HBARs you are going to want to store them in an offline wallet. This is because of the risks that come from large centralised exchange hacks - not your keys, not your Crypto.
Unfortunately, there does not appear to be that much support for HBAR wallets. The few options that you do have include the Hedera Hashgraph mobile wallet, the MyHBAR Browser Wallet, the Hashing Systems browser wallet and the hbarprice.com mobile wallet.
While there is currently no hardware wallet support, this could be around the corner as Hedera states on their wallet page that they expect Ledger Nano support to be arriving soon.
Conclusion
The distributed technology presented by Hedera Hashgraph is revolutionary in what is primarily a blockchain world. The addition of technologies such as virtual voting and the gossip protocol for consensus, as well as aBFT, provide for a secure, fast, and fair network.
The ccodebase may be patented, but it also remains open-source, and anyone can participate in the network, including developers who are free to develop dApps without a license.
Hashgraph has been able to solve part of the scalability problem as well, but only in the number of transactions. It remains to be seen how far it will be able to scale the number of network nodes, which is currently a small number.
Finally, we have to admit that even though the Hashgraph technology is superior to blockchain technology in terms of distributed ledger solutions, that superiority does not guarantee greater adoption. Blockchains are also improving, but I like the potential offered by Hedera Hashgraph and am excited to see what it might become.
Additional Links
Disclaimer: These are the writer’s opinions and should not be considered investment advice. Readers should do their own research.
