QTUM Review: Bitcoin Based dApp Development Platform
Qtum is a project that has been around for some time now. It is also one of the most interesting cryptocurrency to come out of China in the past 3 years.
Originally built to be an "Etheruem Killer", Qtum has been through its own share of ups and downs. However, given the renewed push for blockchain adoption in China, many are turning to projects like this again.
So, does QTUM have the legs to manage the run?
In this QTUM review, I will attempt to answer that with an in-depth overview. I will also take a look at the long term use cases, adoption and price potential of the QTUM tokens.
What is QTUM?
Qtum (pronounced ‘Quantum’) is an interesting blockchain project that’s been in existence since 2016 and was created as a fork of the Bitcoin core combined with Ethereum’s Virtual Machine (EVM).
The resulting blockchain provides us with the best of both Bitcoin and Ethereum, and does it by bridging the gap between the two technologies with a third layer that the Qtum developers have named the “Account Abstract Layer.”

Qtum was created with these three layers in order to serve business users best by combining the Unspent Transaction Output (UTXO) model of bitcoin with the decentralized application (dApp) capabilities of Ethereum. It then wraps them all up in a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus to avoid the huge energy requirements of the Proof-of-Work (PoW) model.
The use of the Ethereum VM gives Qtum a proven and stable development and dApp environment but also brings along the known security and throughput capacity issues.
Qtum solved these Ethereum issues by combining the Bitcoin chain, which is famous for its security. Qtum then adds more services, including a native wallet, a smart contract management application, and oracles that allow off-chain data to be used.
Qtum Technology
As mentioned earlier, Qtum was developed with three separate layers; a fork of the Bitcoin core chain, Ethereum’s Virtual Machine, and the Account Abstraction Layer, which bridges the two technologies and is Qtum’s proprietary development.
Because Qtum uses the EVM it allows for the development of dApps and it can take advantage of Proof-of-Stake as its consensus mechanism, thus getting rid of the need for miners and the huge resource requirements of the Proof-of-Work consensus.
This also means all QTUM tokens are already in existence, having been created at the genesis of the blockchain. Qtum is also able to take advantage of smart contracts thanks to the inclusion of the EVM.
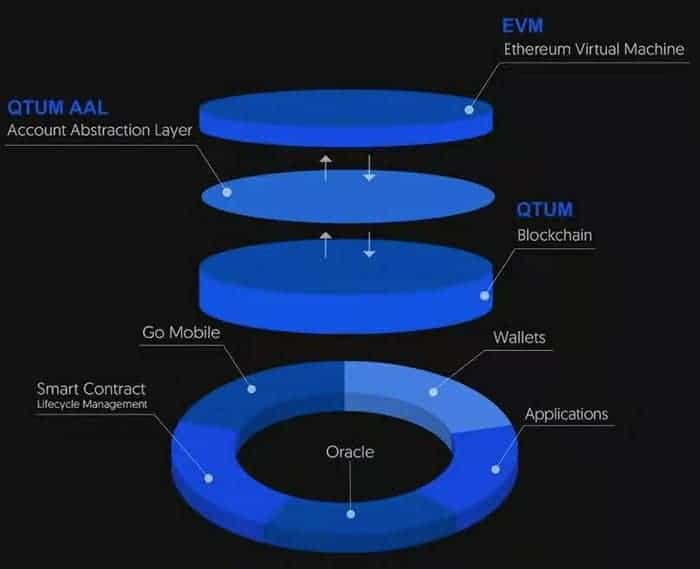
The inclusion of the Bitcoin core chain gives Qtum its solid security foundation through the use of the Unspent Transaction Output (UTXO) model that prevents fraud on the blockchain. It’s this UTXO model brought over from Bitcoin that guarantees transactions cannot be recorded twice. The UTXO model is the basis of Qtum’s security layer.
Because Qtum includes two different blockchains there needs to be a way for the two to communicate with each other. That’s where the Account Abstraction Layer comes in. It functions to convert Bitcoin’s unspent transaction outputs into an “account balance” model, which is what Ethereum uses. This lets the two chains communicate regarding transactions and account balances.
Because Qtum also uses the EVM third-parties are able to create new tokens easily, and it is even possible to automate the management of supply chains. Because Qtum uses a standardized ecosystem it is able to offer tools to create contracts that are both machine and human-readable, and it makes smart contracts both more flexible and less prone to errors.
Key Services
Qtum has also added several key services that make it an ideal blockchain for business use. Below are descriptions of these three key services:
Oracles
Qtum has created oracles that allow trusted external third-parties to supply data and make off-chain calculations, as well as assisting in computations and monitoring the smart contracts on the blockchain. These oracles generate an additional trust layer and make the security for smart contracts stronger.
Mobile Applications
Qtum has also provided for the management of smart contracts from mobile devices. This is something that was once impossible and remains extremely difficult, but Qtum accomplishes it through its use of light clients.
Using this model Qtum is able to run nodes that do not keep a full blockchain history, allowing them to participate on the blockchain by storing only the most recent and relevant transactions.
This is paired with the use of Bitcoin’s Simple Payment Verification (SPV), which allows a wallet to confirm its transactions without needing to verify its full contents. This model greatly increases transaction speeds for devices with minimal computational resources, such as mobile devices.
The QTUM Wallet
Qtum provides a native wallet for users, which isn’t unique by itself, but Qtum has added some unique functionality to its native wallet. The wallet was created to be fully mobile and able to directly interact with the smart contracts on the Qtum chain.
Qtum Unita
In April 2019 Qtum improved further on its blockchain solution by adding a new feature to increase enterprise adoption. The new version of Qtum was dubbed Unita and it utilizes a scalable consensus algorithm (SCAR) that is built atop Qtum’s other existing solutions.
This new SCAR will save considerable network resources such as disk space and bandwidth while creating a fully-automated data storage and transfer protocol that can handle up to 10,000 transactions per second.
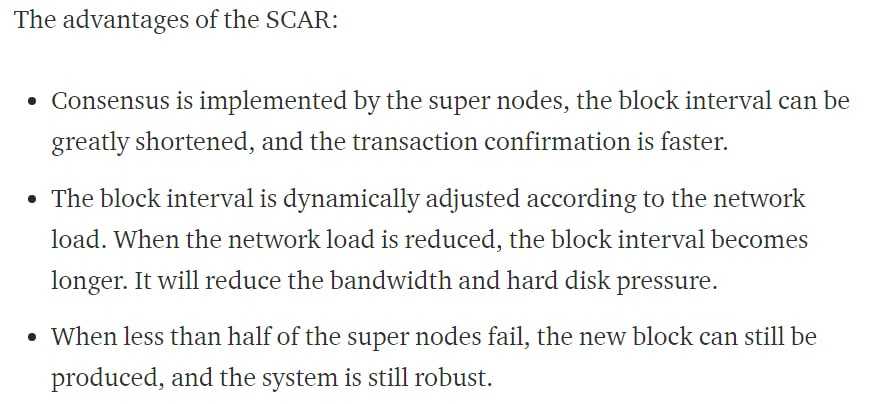
The new Unita can be deployed with just one click and also features data management and cross-chain trading, plus other features that will permit enterprise users to process millions of daily transactions. Qtum said businesses will be able to safely store private data on a permissioned Unita chain, and transfer data as necessary to the public network.
The Qtum Team
Qtum was founded by Patrick Dai, who was an employee at Alibaba when he discovered blockchain technology and became an early adopter and enthusiast of the technology.
Joining him are three dozen other blockchain enthusiasts, including some world-class developers who have come to Qtum with decades of experience in a variety of different sectors.
The team includes a strong group of technology professionals with backgrounds ranging from cybersecurity and telecommunications to full-stack development and blockchain expertise.

Qtum also has a large and experienced group of angel investors and specialists in the capital markets, all of whom have placed their faith, and financial backing, with Qtum. These include Roger Ver, the CEO of Bitcoin.com, and Xu Star, the CEO at OKCoin.
Rounding out the backers is Anthony Di Iorio, the co-founder of Ethereum and CEO at Jaxx Wallet, and Jeffrey Wernick, a veteran of the financial markets with over forty years of trading experience.
Qtum Partnerships
One of the reasons for Qtum’s success to date has been its aggressive moves to partner with major companies, both inside the blockchain space, and within traditional business sectors.
These partnerships have been developed over time, and one of the first major partnerships came in April 2018, when they partnered with the Energo Foundation, a clean energy producer in the Philippines. Energo is using the Qtum blockchain technology yo develop better settlement systems, registrations, and measurements for the local microgrids throughout the Philippines.
Just a few months later in June 2018, Qtum announced a partnership with Qihu360, China’s largest public software company and a specialist in the field of internet security. At the same time, Qtum partnered with another of China’s software leaders, Baofeng.

That partnership is also meant to help Qtum gain 50,000 nodes as well as help developing tools for content distribution and copyright protection. While they’re nowhere near the 50,000 node goal, Qtum does have more nodes than any other blockchain with the exception of Bitcoin and Ethereum. Besides partnering with Qtum, Qihu360 is also helping with blockchain research and the development of decentralized applications.
The following month Qtum announced a partnership with the Celer Network, which was done to integrate the Celer Network’s scalability solutions, giving Qtum faster and more flexible services for the development community.
Qtum also launched on Amazon Web Services the same month, making it easier for businesses already using AWS to migrate to a blockchain solution and build dApps for their operations.
Community
As a relatively mature blockchain project, one would expect to see a large and well-developed community around Qtum, and based on the social media stats you won’t be disappointed. The Twitter following of Qtum is huge, with 181,000 followers. The Facebook following is also pretty large for a blockchain project, with almost 12,000 followers.

As you probably know, Reddit is a popular social network for blockchain enthusiasts, and Qtum is popular over there too, with more than 15,000 followers of the Qtum subreddit. That said, there are some days with no posts, and the number of comments on most Reddit posts is modest.
The Telegram group is approaching 8,000 subscribers, and Qtum also has a presence on Weibo for Chinese speakers. Overall it is a fairly large following, which certainly helps with the spread of information about the project, particularly when they launch something new.
The QTUM Token
The QTUM token is a utility token that is used to access services and make them available to businesses and developers on the Qtum blockchain. This not only includes executing smart contract transactions, but also includes building and provisioning dApps, and executing code. Like most cryptocurrencies, the QTUM token gains value from its use and the overall demand for the token.
Based on the white paper the distribution of QTUM is planned as follows:
80% of the total supply is planned to be distributed to the Qtum community, while the remaining 20% is being earmarked for distribution to the founder, development team, and early backers of the project. Qtum conducted a successful ICO from March 12 through March 17, 2017, raising $15 million by selling QTUM tokens at a price of $0.3000 each.
QTUM Price History
Following the ICO the price jumped over $5 and continued trading higher, remaining in a range of $5 to $20 until exploding in December 2017. By January 7, 2018 the price reached its all-time high of $106.88, but just several days later the price was already cut in half. It continued dropping until bottoming at $1.69 on December 10, 2018.
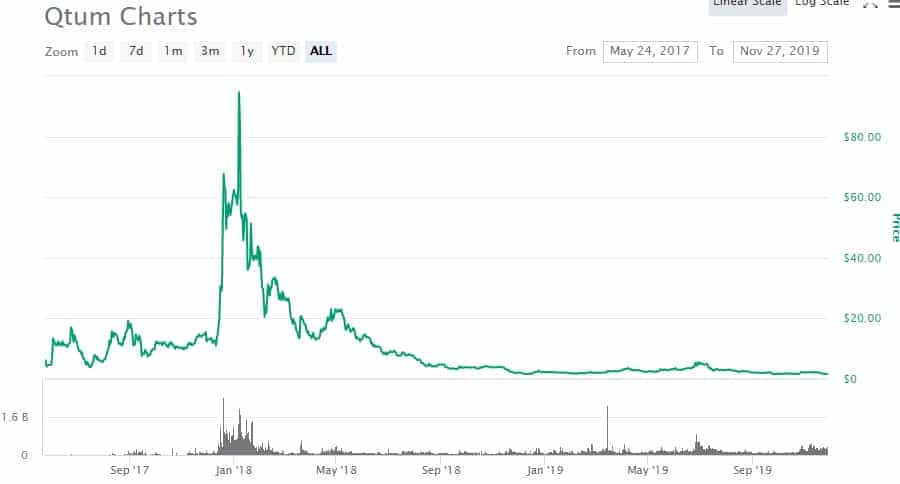
The first half of 2019 saw price rebound, but the strength of the token faded in the second half of 2019, and on September 24, 2019 it hit an all-time low of $1.47. Since then the price has recovered somewhat and as of November 26, 2019 the price of one QTUM is $1.67.
Buying & Storing QTUM
Since QTUM cannot be mined, those who are interested in obtaining or accumulating QTUM will need to begin by purchasing it from an exchange. QTUM is available from a number of exchanges, but cannot be purchased with fiat currency.
Most exchanges are selling it for USDT, BTC, or ETH, although the largest exchange volume is at Cat.Ex, where QTUM is paired with TRX. There is also a good amount of trading volume at IDCM, LBank, and to a lesser extent Binance and Exrates. QTUM is also listed on dozens of other exchanges, but there is very little trading volume at any of them.
Many users choose to store their QTUM in the native QTUM wallet so that they can take advantage of the added features. Those who are more interested in security will be happy to know that both the Ledger and Trezor hardware wallets have support for QTUM.
There are also a number of third party web, mobile and desktop wallets offering QTUM support. These include the Jaxx Liberty wallet and the Atomic Wallet.
Development & Roadmap
So, how much work have the QTUM team been doing on their protocol? Well, perhaps one of the best ways to get a sense of this output is through their open source code repositories.
Hence, I decided to dive into the QTUM GitHub and take a look at their code commits which is the best barometer for raw output. Below are the commits to the top three most active repos over the past 12 months.
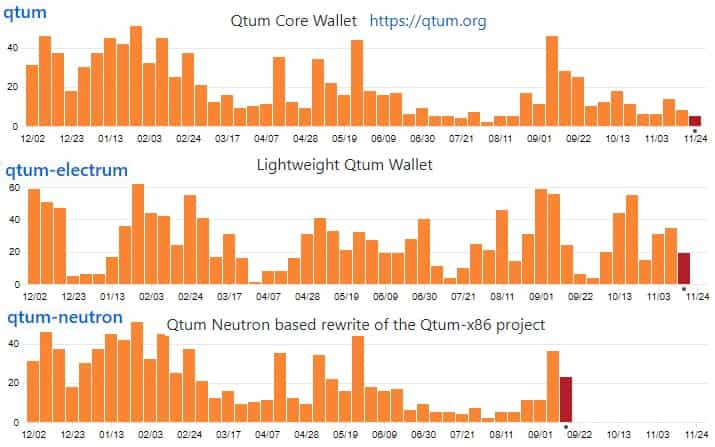
As you can see, there has been quite a lot of development by the team. This is more development work than we have seen at a number of other projects at similar stages in their lifecycle. It is also worth noting that there are over 100 other repos although these have less commits than this.
In fact, if we were to compare the extent of coding activity at QTUM to those of other projects, it ranks quite favourably. For example, on CoinCodeCap, QTUM comes in at number 28 in terms of commits and number 34 for total activity.
Indeed all of this development progress makes sense when viewed in conjunction with the broader roadmap of the project. By the end of Q4 this year, they should have completed Mainnet integration of the x85 VM. They would also have published the first set of trusted library contracts on the mainnet. Finally, they are scheduled for an x86 hard fork as well as a support for new Byzantium op codes.
If you want to keep up to date with the development progress then the team is quite disciplined by posting on their official blog. They also keep their community updated through many of the mediums that I mentioned above.
Conclusion
Qtum is an interesting project that combines the best of the Bitcoin and Ethereum chains and focuses on a light-weight blockchain more suitable to mobile-usage. Bitcoin gives it security and value transfer capabilities, while Ethereum gives it smart contracts and decentralized applications. The combination makes Qtum very valuable for enterprise users, and the success of Qtum has been fueled by these features.
As the first Proof-of-Stake blockchain we know the Qtum team is innovative. The large and growing partnerships show the team’s ability to seek out and secure valuable relationships both within and without the blockchain ecosystem. And the combination of Bitcoin and Ethereum makes Qtum attractive to developers who are looking to move on from those popular platforms.
Taken all together Qtum has positioned itself well for success, living up to the promise of delivering the best of both Bitcoin and Ethereum, and expanding even further on the combination with its x86 virtual machine and the Utica scalable consensus algorithm.
It’s easy to imagine greater things for Qtum as blockchain moves further into the mainstream.
Disclaimer: These are the writer’s opinions and should not be considered investment advice. Readers should do their own research.
