Simple Guide to Ethereum Classic vs. Ethereum: What's the Difference?
If you are relatively new to cryptocurrencies then you may be slightly confused as to what the difference was between Ethereum classic (ETC) and Ethereum (ETH).
They may be mistaken for thinking that they may indeed be one in the same. Unlike Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash, there is only really one Ethereum that is being covered by the mainstream media and all in the community.
We have also covered what Ethereum is and how its blockchain and smart contract protocols are able to facilitate decentralised applications. These use cases are also shared with Ethereum classic.
It is important to note that like Bitcoin and Bitcoin cash, Ethereum classic and Ethereum are the result of a hard fork in the Ethereum network. However, in this case the coin that forked away from the established chain was Ethereum and not Ethereum classic.
This was as the result of an action in necessity and is more about underlying politics than anything else. Let’s take a deeper look into these two coins.
We start our piece on the beginning of the story, the DAO...
The DAO Ecosystem

The DAO (Decentralised Autonomous Organization) was a developed as an Ethereum smart contract that was going to revolutionise the way we thought about Etheruem. The idea behind it was to be a decentralised venture capital fund that would invest in potential dApps and earn returns for the initial investors.
Those that would have bought into the DAO would have received DAO tokens. These could be thought of as shares that one would have in a Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) that would invest in real estate deals on your behalf.
These DAO tokens would also confer the holders voting rights in any of the investments that they were interested in. These token holders could vote on the projects that they had the most belief in. Those projects that had the most votes would then get "whitelisted" and receive the investments.
This was seen as an amazing project and attracted a great deal of interest from thousands of investors. In total, the DAO crowd sale was able to raise about $150m in ETH within only 28 days. It was also estimated that at least 15% of all Ethereum in circulation was invested in the DAO.
In order to give users the option to opt out of any investment that they really disapproved of, they could exit it through something called the "split function". This would allow the investor to get back the Ethereum that they had invested and create a "child DAO".
However, this also had one critical flaw in that it could also be used by a hacker to extract funds. This was viewed by many as a loophole that was not corrected and eventually lead to the creation of Ethereum Classic.
The Infamous DAO Hack
Low and behold, a hacker was able to make the most of this particular vulnerability. They were able to hit the DAO and take away about a third of the funds that were invested. The vulnerability was really quite simple in that the hacker was able to construct a recursive function in the splitting request.
The result of this was that the hacker would make a request for the funds to be sent to them for their own child DAO. However, before the internal balances could be updated the function would run again and extract even more Ethereum.
This could not be stopped and allowed the vulnerable code to extract about $50m ETH to the Child DAO that he / she had set up. When such a large amount of funds was stolen, this would no doubt have a massive impact on the relatively new Ethereum community.
Until the Parity multisig hack at the end of 2017, the DAO hack was the biggest Ethereum hack to date and the price of ETH collapsed as many wondered what this could mean for the stability of the coin. They were concerned that the hack was as a result of wider vulnerabilities in the network.
However, this was a coding error on the part of the DAO and many in the Ethereum community viewed it as such.
What to do About the Hack

Even though this was an error in the code of the DAO smart contract, the hack still had the effect of swaying people’s faith in the broader Etheruem project. The notion that over $50m in Ethereum could so easily be stolen from sloppy code was hard to comprehend.
There was as slight saving grace period and that was the 28 days waiting period that the hacker had to wait in order to take out his ETH. With this period free for the response from the developers. During this time, they had to think of a potential solution to the problem.
There were a number in the community who viewed the mistake on the part of the DAO and that there should be no response from the community. They claimed that the notion of a blockchain is that it is immutable and hence cannot be changed.
However, there were many who wanted to lock down the funds of the hacker and make sure that he would not be able to move them out in any transaction. They then considered a soft fork solution.
Potential DAO Soft Fork
This was seen as the most likely solution as it would allow for the hacker to be locked out from the network. Yet, the change to the Ethereum code would also be backwards compatible. This would mean that all of the nodes could still operate without instituting the change.
On paper, this sounded like a great solution. However, there was one thing that they had not considered and that was the potential for a DOS (Denial Of Service) attack on the Ethereum network. This could have paralysed the Ethereum network and left it inoperable.
Essentially, the Ethereum network requires miners to be rewarded for computational work through GAS. This is the cost for a transaction and it is developed in order to make spam or numerous transactions too costly. This was the manner in which DOS attacks could be thwarted.
However, given the nature of this soft-fork, the attacker can send transactions with no GAS. He can therefore afford to send numerous transactions and flood the network with complicated transactions that interact with the DAO. The result would be a DOS attack on the network.
Hence, the only way for the Ethereum community to effectively shut the hacker out of his funds would be to implement a much more rigid hard-fork.
The Hard Fork Solution
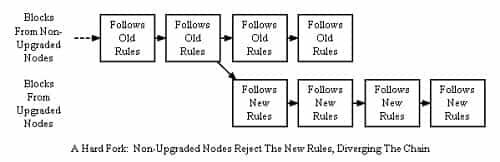
A hard fork differs from a soft fork in that the changes are not backward compatible. This means that once the fork is implemented, no nodes can operate on the older code base. They will all have to update or face being made redundant and unable to interact with the broader network.
In the case of Ethereum, this hard-fork would have been implemented on the block that was just prior to the DAO attack. In this case it was at block 1,920,000. This would mean that prior to this block, the old and the new chain are the same. After this fork, they are completely different.
On the creation of the new chain, the developers would have run a smart contract that would have returned all of the funds that the DAO was able to raise and give them back to the members who had funded.
This caused a great deal of disagreement in the community. Many were of the view that this went contrary to the notion of decentralisation. They were opposed to the idea that a group of developers could change network rules and "reward" bad coding.
These developers also thought that if there was no cost to the hack on the part of the developers and those who had funded into the DAO, then it would create a precedent for future failures. It could provide negative externalities as there were no costs for improper code audits.
This disagreement was what led to the launch of Ethereum Classic.
Ethereum Splits from Ethereum Classic
Most of the biggest players in the Ethereum ecosystem including the most influential developers supported the forking of Ethereum. For example, both Vitalik Buterin and Gavin Wood who are the founders decided that this was the best course of action to take.
Nevertheless, there were still a number of those in the community who viewed the hard fork as contrary to the ideals that dominate cryptocurrency. They view the intervention of the developers in one hack after another as an example of negative externalities.
There were also some influential people who were behind Ethereum Classic (ETC) including the CEO of Grayscale, Barry Silbert. They kept the initial code and decided to avoid the changes that the main Ethereum network had implemented through the fork.
Now that we know all of the circumstances that led to the fork, let’s compare the two coins
Ethereum Classic vs Ethereum
If one was to look at the performance of both coins since the DAO hack and the hard fork it is quite clear that Etherueum (ETH) has substantially outperformed Ethereum Classic (ETC). You can see the price comparison of the two chains in the chart from coin market cap below.
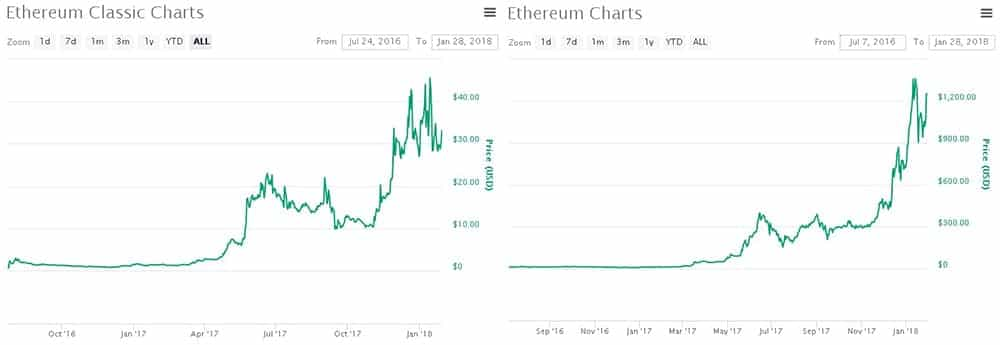
This is due to a number of reasons that the Ethereum classic deveopers would no doubt of known. Given that the hard fork is not backwards compatible, any changes that are implemented on the Ethereum network can will not be compatible with the Ethereum Classic chain.
Since the split from the Ethereum classic, the main ETH chain has undergone a number of fundamental changes and improvements which include mining changes, confidential transactions etc. These were all outlined in the Metropolis upgrade that has been underway for some time.
These updates and the range of dApps and ICOs that have been built on the Ethereum ecosystem have further driven mass adoption for the ETH chain. The result of this mass interest has been that the price of Ethereum has continued to rally and reach all time high prices of over $1,300.
Moreover, with the release of the Byzantium update and the eventual implementation of Casper Proof-of-Stake (POS) mining, the price is likely to continue rallying.
Hence, if you were considering whether to invest in Ethereum or Ethereum Classic, you have to take into account that all of the updates that have taken place with ETH since the hard-fork are not going to be part of the Ethereum ETH chain.
Although technically, the Ethereum ETH chain is superior, from an ideological perspective it has still left a bad taste in many people’s mouths. Indeed, we saw this recently play out in the parity incident as the community was split on whether the they should implement any code changes to save the frozen funds.
As was expected in that case, there was a simple coding error on the part of Parity and as they were requesting a hard fork many were thinking back to the precedent that was set from the DAO rescue. Nevertheless, it seems as if the main developers will not support a hard fork in this case.
Many claim that this is the reason that the Ethereum classic ETC chain was the more ideologically pure. They will never bail out any badly coded dApp on their network.
Of course, one will also have to take into account how the switch of Ethereum from Proof-of-Work (PoW) mining to POS mining will have on the miners who are currently on the Ethereum network. It is indeed quite likely that these miners may switch to the Ethereum classic chain in the event that they cannot be a master node.
Conclusion
Although the Ethereum classic chain was meant to be the more ideologically pure than the Ethereum chain, it has not kept up with the pace of development of the ETH.
This is something that the Ethereum classic developers are desperately trying to change and this is evidenced by the total number of commits to the GitHub repository in 2017. It was ahead of Ethereum at 895 compared to Ethereum's 883.
This is one of the reasons that people think that an Ethereum classic investment in 2018 has alto of potential to provide impressive returns. Moreover, given that Ethereum is already the second most valuable cryptocurrency by market cap, the chance for greater returns are mathematically more difficult.
On the flip side though, there are many less places where new investors can buy Ethereum classic than they can Ethereum ETH. Currently Ethereum is on nearly every Fiat exchange like Coinbase, Bitstamp etc. Currently Ethereum Classic in on only a few such as Kraken exchange etc.
Hence, these market factors together with the ideological / technological factors need to be considered when determining an investment between Ethereum Classic and Ethereum.
Disclaimer: These are the writer’s opinions and should not be considered investment advice. Readers should do their own research.
